The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) guidelines contain strict rules for how organizations must handle personal data breaches.
These guidelines are essential for organizations to understand when and how to notify the relevant supervisory authority and affected individuals during a data breach, including incidents involving the accidental or unlawful destruction of personal data.
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the GDPR breach notification rules, including definitions, types of breaches, when and how to notify the relevant authorities and affected individuals, and how tools like Fyno can help ensure compliance.
What is a personal data breach?
A personal data breach occurs when a security issue results in customers’ personal data being accidentally or unlawfully destroyed, lost, altered, disclosed, or accessed without permission, affecting the data subject.
This can include breaches resulting from internal and external threats and affect personal data breach including confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
The importance of timely breach reporting
Under GDPR, timely reporting of data breaches without undue delay is crucial to minimize potential harm to individuals and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Prompt notification allows affected individuals to take necessary precautions to protect their personal data records concerned with maintaining trust in the organization’s data protection practices.
Types of personal data breaches: confidentiality, integrity, and availability
Based on their nature, personal data breaches are classified into three broad categories:
Confidentiality breach: When personal data is seen or shared without permission.
Integrity breach: When personal data is changed without permission.
Availability breach: When personal data is lost or inaccessible when required.
Examples of personal data breaches
A laptop with unencrypted personal data is stolen.
A hacker gains unauthorized access to personal data.
Important personal data was accidentally deleted, and there is no backup.
Unauthorized access to personal data transmitted over an unsecured network.
Reporting requirements and procedures
The 72-hour deadline and notification requirements
If you know of a personal data breach within your organization, Article 33 of GDPR mandates that you notify the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours. If notification is not made within 72 hours, it must be accompanied by reasons for the delay.
One such instance is when the personal data affected by the breach is encrypted and the encryption key remains uncompromised.
Necessary steps for developing a data breach response plan
Despite careful measures, there is always a chance of a data breach within your organization. To be on the safer side, it is advised to develop a comprehensive data breach response plan.
Here are the things you should do to make an effective data breach response plan.
Establishing a breach response team.
Defining the roles and responsibilities of everyone in the response team.
Setting up guidelines for incident detection and reporting procedures.
Conducting regular training and simulations.
Performing regular information security audits to identify missed breaches and other vulnerabilities
Reviewing and updating the plan periodically.
Who should be notified after a data breach?
After a data breach, notifications should be sent to:
Supervisory authorities: As mentioned above, within 72 hours of a breach, you must inform the supervisory authority about the incident. The authority might vary based on your region — the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK and the Data Protection Agency (DPA) if it’s the EU region.
Data subjects: Besides notifying the supervisory authorities, you should notify those whose data is affected by the breach. Notifying affected data subjects is crucial, especially when the breach is likely to result in a high risk to individuals' rights and freedoms, necessitating direct and prompt notification.
Other entities: Data processors, insurers, and legal advisors, as necessary.
It is crucial to report incidents that pose a significant risk to the data subjects concerned.
Notification content and communication
Essentials of a data breach notification
A data breach notification should include the following.
A description of the nature of the breach.
The categories and approximate number of data subjects and records affected.
Likely consequences of the breach.
Contact details of the data protection officer or other contact point.
Measures taken or proposed to address the breach and mitigate its effects.
If all the information isn't available at once, it can be provided in stages as long as there is no further undue delay.
Communicating a breach to data subjects
Organizations must inform affected individuals about a personal data breach. The notification to individuals should include the following:
A description of the breach.
The likely consequences of the breach.
Contact details of the data protection officer or other contact point.
The measures taken or proposed to address the breach and mitigate its effects.
The notification should be clear and concise to ensure that the concerned data subjects understand the potential risks and the measures to mitigate them.
Exceptions and special cases in breach notification
There are exceptions to breach notification requirements, such as:
If the data was encrypted or otherwise protected in a way that makes it inaccessible to others.
If measures have been taken to ensure the high risk to data subjects’ rights and freedoms is unlikely to materialize.
Legal and financial implications
Potential fines and regulatory actions
Non-compliance with GDPR’s breach notification requirements can result in significant fines and regulatory actions. Fines can reach up to €10 million or 2% of the organization’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
Breach documentation requirements
Organizations must keep records of all personal data breaches, even if they do not need to notify the supervisory authority. These records should include details about what happened, the effects, and the actions taken, etc.
Can supervisory authorities mandate notifications?
Yes, supervisory authorities can mandate notifications if they believe the breach poses a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals, even if the organization initially deemed the risk low.
Practical steps for compliance and prevention
Formulating a personal data breach response strategy
An effective data breach response strategy should include:
Immediate containment and recovery actions.
Thorough investigation and documentation of the breach.
Communication plans for notifying affected parties.
Review and improvement of security measures to prevent future breaches.
Preventive measures to avoid data breaches
Preventive measures include:
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Employee training on data protection and breach response.
Implementation of strong access controls and encryption.
Continuous monitoring and incident detection systems.
Role of data processors in breach notifications
Upon becoming aware of a personal data breach, data processors must notify the data controllers immediately.
But who is a data processor, and who is a data controller? Let's use a simple example to understand the roles:
Imagine TechStorez, an online retailer, uses a company called PaySecureD to handle their customers' payment information.
TechStorez is the data controller because it decides why and how customers' personal data is used.
PaySecureD is the data processor because it processes payment information on behalf of TechStore.
Now, if PaySecureD discovers a data breach that affects the payment information they handle for TechStorez, here's what happens:
PaySecureD (the data processor) must inform TechStorez (the data controller) when they become aware of the breach.
TechStorez (the data controller) must then report the breach to the relevant supervisory authority (like a data protection agency) immediately and within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach.
If necessary, TechStorez must also inform the affected customers about the breach.
This process ensures that the entity responsible for deciding how the data is used (TechStorez) communicates with authorities and customers while the entity handling the data (PaySecureD) quickly informs them of any issues.
How fyno enhances GDPR compliance in data breach notifications
Ensuring GDPR compliance with data breach notification requirements is crucial for protecting personal data and avoiding significant legal repercussions. Fyno provides several features to help organizations streamline compliance efforts and manage data breaches effectively.
Robust security features
Fyno offers advanced security measures designed to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with GDPR regulations. These include:
Masking
Masking is a feature that covers sensitive data points when displayed within Fyno.
When activated, it ensures that data payloads and destination details are stored in plaintext but displayed in a masked format (e.g., "xxxxx").
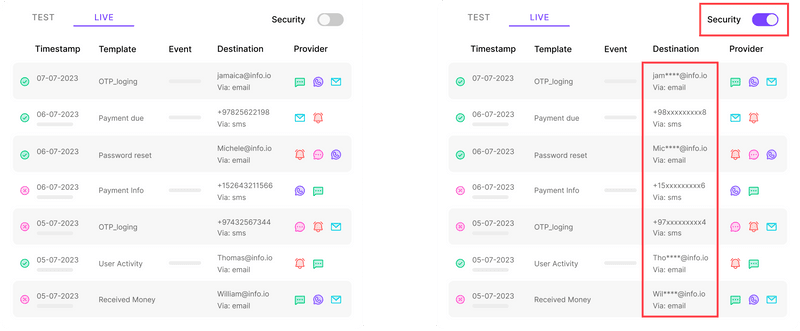
This feature helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access while allowing authorized users to unmask the data when necessary.
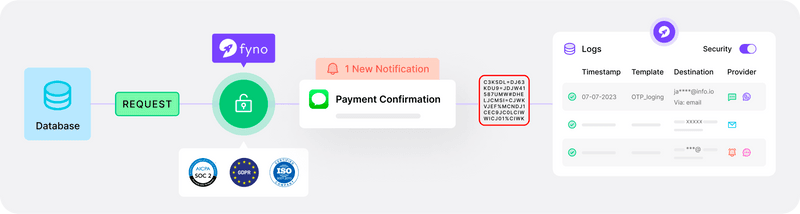
How it works:
Fyno receives an API request containing sensitive data.
If masking is enabled, the data is stored in plaintext but displayed as masked data in logs and reports.
Authorized users can unmask the data when needed.
Hashing
Hashing is an irreversible process that permanently hides sensitive data points by converting them into a hashed format.
Once applied, the hashed data is stored in the database and displayed as "[redacted]" in Fyno.
This ensures that sensitive information remains protected, even if unauthorized parties access the data.
How it works:
Fyno receives an API request with sensitive data.
If hashing is enabled, the data is hashed before being stored in the database. The hashed data is displayed as "[redacted]" in logs and reports.
Unlike masking, hashed data cannot be reverted to its original form.
Push token cleanup
Fyno's push token cleanup feature helps maintain clean and relevant data by removing outdated or unused push tokens from user profiles. This ensures that only the latest and necessary data is retained, reducing the risk of data breaches and enhancing overall data security.
How It Works:
The push token cleanup feature identifies and removes outdated push tokens from user profiles.
This helps keep user data up-to-date and minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to outdated tokens.
Comprehensive logging and monitoring
Fyno provides detailed logging and monitoring capabilities that help organizations track and manage data breaches effectively.
Key monitoring features:
Sent logs: Track all outgoing notifications and their statuses.
Event logs: Monitor events that trigger notifications and their outcomes.
Automation logs: Keep records of automated processes and their results.
These logs ensure compliance with GDPR's documentation requirements and provide necessary information to supervisory authorities when needed.
Simplified notification management
Fyno's centralized template management and cross-channel workflow automation make it easier for organizations to send breach notifications. By using Fyno, businesses can ensure that notifications are sent promptly and consistently across all communication channels, meeting GDPR's 72-hour notification requirement.
Conclusion
Understanding and complying with GDPR data breach notification requirements is essential for protecting personal data and avoiding significant legal and financial repercussions. By implementing robust response plans and leveraging tools like Fyno, organizations can enhance their breach management processes and ensure timely and effective notifications.
FAQs
1. What is a personal data breach under GDPR?
A personal data breach occurs when personal data is accidentally or unlawfully destroyed, lost, altered, disclosed, or accessed.
2. When must a personal data breach be reported?
A personal data breach must be reported to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours.
3. Who should be notified in the event of a data breach?
Both the relevant supervisory authority and the affected individuals must be notified.
4. What information should be included in a data breach notification?
The notification should include the nature of the breach, affected data categories, consequences, and measures taken.
5. What are the potential fines for non-compliance with GDPR breach notification requirements?
Fines can reach up to €10 million or 2% of the organization’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
6. What is the role of a data processor in breach notifications?
A data processor must immediately notify the data controller upon discovering a breach.
7. Are there any exceptions to the breach notification requirement?
Exceptions include when the data was encrypted or if measures have been taken to ensure the high risk to data subjects is unlikely to materialize.
8. How can Fyno help with GDPR compliance in data breach notifications?
Fyno provides advanced security features, comprehensive logging, and centralized notification management to streamline compliance efforts.