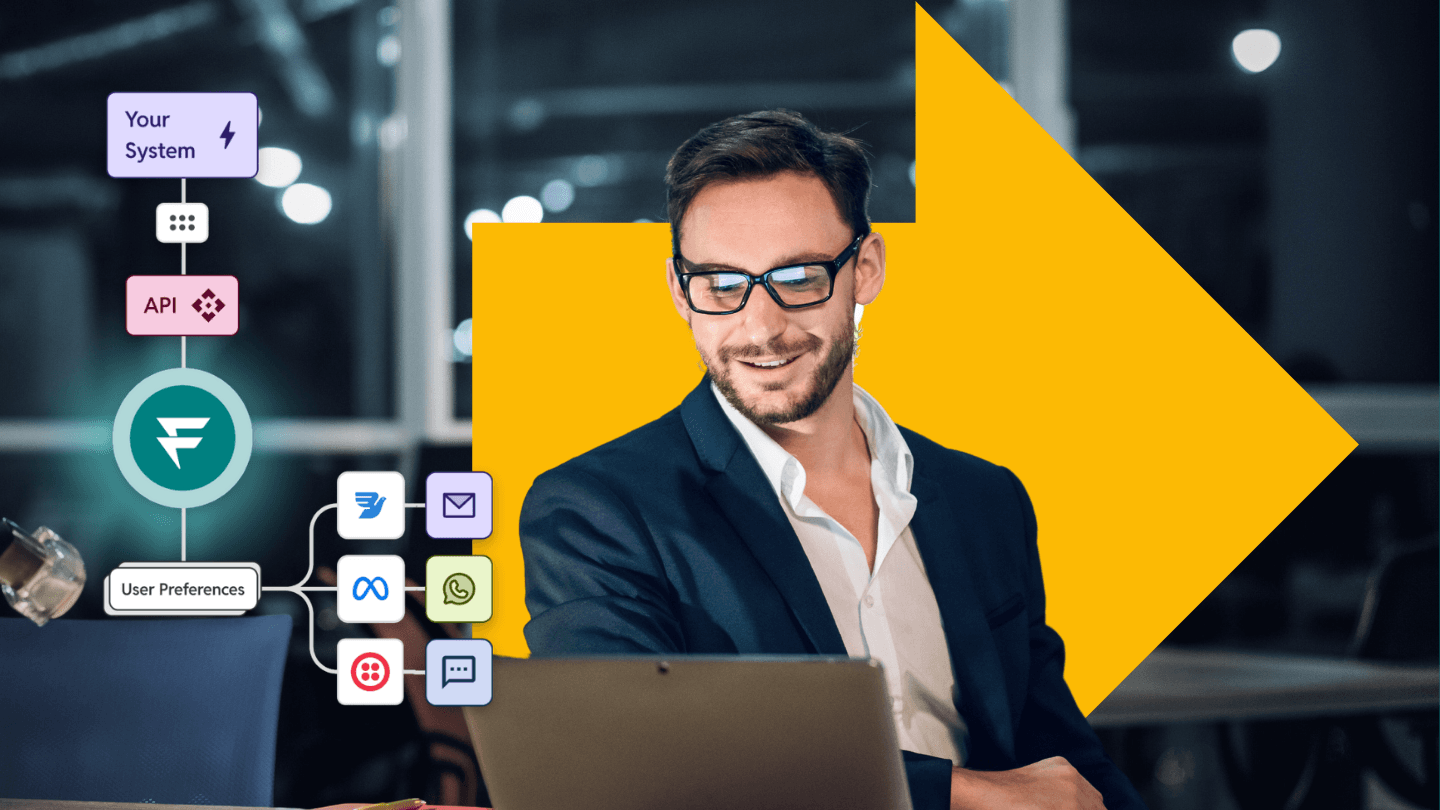
Ever wondered how you can send sensitive data without it falling into the wrong hands? Now, imagine sharing sensitive info and not knowing who else might be reading it. Scary, right?
That’s where end-to-end encryption (E2EE) steps in. However, without E2EE, your data is like a postcard anyone can read. Hackers, cybercriminals, and even nosy intermediaries could intercept and access your private information. This can lead to serious consequences, from identity theft to financial losses.
Take the infamous 2013-14 Yahoo data breach, for example. Hackers exposed data from billions of accounts, leading to a massive fallout. This catastrophe highlighted the dire need for robust encryption.
In a world where data breaches are becoming more common, E2EE ensures your messages stay private and secure. Let's understand it in detail.
Understanding end-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryptioEnd-to-end encryptionn ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the messages. It converts sensitive data into scrambled text that remains unintelligible without a specific secret key.
So, what makes RCS stand out in terms of security?
- Encryption: RCS aims to encrypt messages, making them unreadable to anyone but the intended recipient.
- Enhanced features: Beyond basic texting, RCS supports high-quality pictures, videos, and even location sharing—all while keeping your data secure.
- Read receipts and typing indicators: Know when your message is read and when someone is typing back without compromising security.
Why does this matter?
- Prevents unauthorized access: Your data stays private, even if intercepted.
- Ensures confidentiality: Only the intended recipient can decrypt the message.
- Boosts trust: Users know their information is secure.
End-to-end encryption isn't just a buzzword. It’s a fundamental feature ensuring the security and privacy of digital communication. Next time you send a message, remember the layers of protection working behind the scenes to keep your data safe.
Evolution and adoption of RCS messaging
RCS uses advanced algorithms to ensure that even if someone intercepts your message, they can't read it. The technical side is fascinating. RCS uses a method called "Diffie-Hellman key exchange" to securely share encryption keys between devices. This method ensures that even if someone is eavesdropping, they can't figure out the exchanged keys. This method ensures that every message remains private and secure.
End-to-end encryption in RCS (Rich Communication Services) is a game-changer for secure messaging. Here's how it works:
- Encryption keys: When you send a message, it gets encrypted with a unique key. Only the recipient’s device has the matching key to decrypt it.
- Key exchange: Before communicating, both devices exchange encryption keys securely. This ensures that only the intended devices can decode the messages.
- Group chats: In group chats, each participant has their own encryption key. Messages get encrypted for each key, ensuring everyone’s privacy is intact.
The history and development of RCS
Unlike SMS, which is text-based and limited, RCS supports images, videos, file transfers, and interactive elements. This makes it super useful for businesses wanting to engage with their customers more meaningfully. For more insights on why traditional SMS still holds dominance in certain regions like India, you can read our article on the enduring dominance of SMS in the digital age.
RCS has had quite the journey. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Early 2000s: The idea of RCS was born to upgrade the ageing SMS protocol.
- 2007: The GSMA (GSM Association) started working on standardizing RCS.
- 2012: The first commercial launches of RCS in South Korea and Spain.
- 2015: Google acquired Jibe Mobile, an RCS tech leader, which was a game-changer.
- 2016: Google launched its RCS-based messaging app in the U.S., pushing carriers to adopt the new standard.
- 2020: Google enabled RCS globally via its Messages app, bypassing some carrier limitations.
Due to carrier dependencies, RCS adoption has been a bit slow, but it's gaining ground rapidly. The aim is to have a universal standard that works seamlessly across different carriers and devices.
RCS is set to revolutionize how we think about traditional text messaging, offering a richer, more interactive experience. For businesses looking to explore other rich messaging platforms, you might find it useful to consider nine essential communication channels for digital businesses to enhance customer engagement.
Current challenges in RCS encryption
While RCS can be end-to-end encrypted, there is still a gap. The core RCS protocol doesn’t have default end-to-end encryption (E2EE), exposing messages. This means your message content and metadata are accessible to phone companies and law enforcement.
What’s the deal with this lack of encryption?
- Metadata accessibility: Even without reading your message, metadata reveals who you talk to, when, and how often. This can be exploited for surveillance or targeted attacks.
- Interception risks: Unencrypted messages can be intercepted, leading to potential data breaches.
- Carrier and government access: Without E2EE, carriers and governments can easily access your messages. They prefer this for surveillance and security reasons.
Remember the AT&T data breach? It’s a prime example of what can go wrong when encryption isn’t a priority.
Now, Google stepped in with its version of encryption using the Signal protocol. But it’s not a perfect fix.
- Google's implementation: This encryption works only if both users are on Google Messages.
- Key server dependency: It relies on Google’s central key server for key exchange.
- Carrier support: Both users’ carriers need to support RCS for encryption to work.
- Blocking: Carriers can block this encryption.
- Metadata: The encryption doesn’t cover metadata, so some data remains exposed.
Experts argue RCS should have had E2EE from the start. The current setup leaves a lot to be desired in terms of privacy.
Google's attempt to add encryption helps but isn't universal. It requires both users to be on Google Messages and relies on Google's key server. This still leaves some data, like metadata, exposed. The core RCS protocol still has significant security gaps that need addressing.
Recent developments and updates (Universal Profile 2.7)
RCS is continually evolving. The latest update, Universal Profile 2.7, brings some exciting features that make messaging more interactive and secure.
- Enhanced messaging: You can now enjoy a richer messaging experience with features like high-res photo sharing and larger file transfers.
- Message editing and recall: Sent something you didn’t mean to? No worries. Edit or recall messages even after they’ve been sent.
- Advanced reactions: Express yourself better with a wider range of message reactions.
Privacy and compliance
Encrypted communications are essential for meeting compliance standards in regulated industries. Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA mandate stringent privacy requirements.
- Regulatory compliance: Meets legal standards for data protection.
- Audit trails: Provides traceable communication logs for compliance checks.
- User privacy: Ensures user data remains confidential and protected.
For businesses in healthcare, secure RCS messaging means patient information stays private. In finance, it's about protecting client data and maintaining trust. Compliance isn't just about avoiding fines; it's about showing your commitment to user privacy.
Just as RCS supports stringent compliance with regulations, SMS communications must also meet regulatory standards. Discover more about SMS compliance laws and best practices.
Technical specifications and standards for RCS encryption
RCS encryption relies on strict technical standards for secure messaging. The GSMA plays a key role in setting these standards. Their Universal Profile provides a consistent framework for RCS across carriers and devices.
Role of mobile network operators and device compatibility
Mobile network operators (MNOs) are crucial for RCS. They put the GSMA standards into practice, making RCS available to users. MNOs handle:
- Standard compliance: Following GSMA guidelines for RCS features.
- Security protocols: Using encryption to protect messages.
Device compatibility is a hurdle. Android has embraced RCS, but iOS lags behind. Work is ongoing to close this gap.
To boost compatibility:
- Cross-platform support: Developers are creating solutions for RCS on different operating systems.
- Carrier teamwork: Operators work together to give users a smooth experience, no matter their device.
For businesses looking to enhance their communication strategies, choosing the right notification system that integrates various channels, such as email, SMS, and push notifications, is essential. This integration ensures effective messaging and improved decision-making through advanced analytics.
Despite these issues, RCS use is growing. As more carriers and device makers adopt RCS, we move towards a universal, secure messaging standard.
Implementing RCS encryption
Setting up RCS encryption is straightforward. Here's a quick guide:
- Check compatibility: Ensure your messaging app and carrier support RCS. Not all devices and networks are ready for RCS yet.
- Update software: Make sure your apps and devices are running the latest software versions. Updates often include essential security patches.
- Enable RCS: Go to your messaging app settings. Look for the option to enable RCS or chat features.
- Verify encryption: Once RCS is enabled, check if end-to-end encryption is active. Most apps will display a lock icon or similar indicator.
- Configure group chats: If you use group chats, ensure each participant’s device supports encrypted RCS. This ensures everyone’s messages are secure.
These steps help businesses quickly set up secure messaging. Keeping software updated and verifying encryption is critical for maintaining security.
Challenges and considerations
Implementing RCS encryption isn't without its hurdles. Here are some common challenges and tips to handle them:
- Interoperability issues: RCS works best when all parties use compatible devices and networks. Encourage your customers to update their devices and carriers to support RCS.
- User experience: Encryption can sometimes delay message delivery. Make sure your users understand the importance of these security measures.
- Data privacy regulations: Different regions have different data privacy laws. Ensure your RCS implementation complies with local regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Carrier limitations: Some carriers may not fully support RCS features. Work closely with your carrier to troubleshoot and resolve any issues.
For businesses looking to explore alternatives to traditional messaging systems, understanding why WhatsApp is becoming a popular choice for transactional notifications can provide valuable insights.
Addressing these challenges ensures a smooth and secure messaging experience. With thoughtful implementation, businesses can leverage RCS encryption for reliable and secure communication.
Comparing RCS encryption with other messaging apps
RCS encryption stacks up well against WhatsApp, Signal, and iMessage. Let's see how these platforms compare to RCS.
- WhatsApp: WhatsApp offers end-to-end encryption for messages, voice, and video calls. It's privacy-focused but needs internet and a separate app. RCS, on the other hand, works right in your phone's default messaging app.
- Signal: Signal is the go-to for security buffs. It uses end-to-end encryption and is open-source, letting anyone check its code. Again, similar to WhatsApp, you need to download it, whereas RCS comes built-in.
- iMessage: Apple's service encrypts messages end-to-end, but it only works on Apple devices. It's smooth within the Apple world, but talking to non-Apple users can be tricky. RCS aims to work everywhere.
RCS brings together the best parts of messaging. It's as simple as SMS but can do more, like share media and show read receipts. And it does all this with end-to-end encryption.
Future of RCS encryption
RCS encryption needs an upgrade. Future advancements must focus on making encrypted communication the default. Apple plans to support RCS in iOS 18 starting in 2024. This move aims to improve interoperability between iPhone and Android users. Apple's goal? To incorporate encryption into the RCS standard.
The GSMA, the global association for mobile operators, is crucial here. They need to adopt modern cryptographic standards, including protecting metadata and preventing downgrade attacks. The shift to better encryption can't happen without their involvement.
Legal challenges are part of the equation. Law enforcement and governments often oppose strong encryption, arguing it hinders their ability to monitor communications for security purposes. This creates a tug-of-war between privacy advocates and regulatory bodies.
Here's what the future could look like:
- Interoperable encryption: Encrypted messaging should work seamlessly across all devices and carriers.
- Metadata protection: Encryption should cover not just messages but also metadata.
- Strong cryptographic standards: Adopt robust standards to prevent downgrade attacks and ensure secure communication.
- Legal advocacy: Ongoing efforts to balance privacy and regulatory needs.
In short, the future of RCS hinges on stronger encryption standards and widespread adoption. The goal is clear: secure, private communication for everyone.
Key takeaways
RCS encryption is a mixed bag. While it offers modern messaging features, its lack of default end-to-end encryption (E2EE) raises serious security concerns. Here's a quick recap:
- Current state: The core RCS protocol doesn't include default E2EE, leaving message content and metadata exposed to phone companies and law enforcement.
- Google's effort: Google has implemented E2EE using the Signal protocol, but it only works if both users are on Google Messages and rely on Google's key servers.
- Privacy risks: Without E2EE, your messages can be intercepted, and your metadata can be scrutinized, posing privacy risks.
The future of RCS encryption hinges on several factors:
- Interoperability: Encrypted messaging needs to work seamlessly across all devices and carriers.
- Metadata protection: Encryption must cover not just the messages but also the metadata.
- Strong standards: Adopting robust cryptographic standards is essential to prevent downgrade attacks and ensure secure communication.
- Legal balance: A balance between privacy and regulatory needs requires ongoing advocacy and dialogue.
While RCS has the potential to enhance user experience with advanced features, its security gaps need to be addressed. The push for better encryption standards and widespread adoption is key to making RCS a secure and reliable communication tool.
Conclusion
RCS encryption has made significant strides, but it's not perfect yet. The core tech of RCS doesn't have end-to-end encryption (E2EE) baked in, though Google is actively working on it. This gap means businesses need to be cautious about the type of communications they send via RCS.
What can be sent safely? Non-sensitive communications like promotional messages, appointment reminders, and general updates are good to go. These don't require the extra layer of security that E2EE provides.
Relying solely on RCS might not be the best move for sensitive data, like financial transactions or personal details. To ensure data protection, alternative secure channels, like encrypted email or apps with built-in E2EE, should be considered.
Despite this, RCS still offers a robust platform for enhancing customer communication. The rich features like high-res photos, read receipts, and typing indicators can significantly improve user engagement. Plus, with Fyno's infrastructure, managing these communications becomes straightforward and dependable. Let's see how?