What is SMS security, and why is it important?
If you’re a business owner, you have a variety of communication channels to choose from — Channels that are advanced, secure, and affordable. But, SMS is still the number one choice for businesses when it comes to implementing 2FA.
Reason? It’s simple, time-tested, and doesn’t require the users to have a smartphone or internet connectivity — which is why banks, financial institutions, government portals, and other critical services use SMS to verify their users.
With millions of businesses and government bodies relying on SMS, we should look into the vulnerabilities of using SMS as an authentication channel and assess their impact? Because failing to address the vulnerabilities in SMS security could lead to various implications including data leaks, scams, theft, and fraud.
In this blog post, let’s dive deep into common SMS security risks and vulnerabilities, benefits of using SMS as an authentication method, and also look into how platforms like Fyno help you protect user information, maintain deliverability rates, without compromising on SMS security.

Let’s begin.
Common SMS security risks and vulnerabilities
While SMS offers convenience and accessibility, it also comes with its own set of security vulnerabilities. Here are some common SMS security risks to be aware of:
SMS spoofing
SMS spoofing occurs when an attacker uses techniques to send messages to make it look like it is coming from a trusted source. SMS spoofing is commonly used in phishing attacks to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information.
SMS interception (or) Eavesdropping
SMS messages can be intercepted by malicious actors by exploiting the existing vulnerabilities of various mobile carriers. And, since SMS messages are not encrypted, hackers use SMS interception is used to read the contents of the messages and potentially steal sensitive data like One-time Passwords/Pins (OTP), credit card details, etc.
SMS phishing (SMiShing)
SMiShing is a variant of phishing attacks that specifically target SMS users. Attackers send deceptive messages claiming to be from legitimate organizations, luring recipients into clicking malicious links, which could lead to revealing sensitive information like credit card information or passwords or leading to a financial loss.
SMS flooding
SMS flooding, SMS bombing, or SMS flood attack is a type of denial-of-service attack where a large volume of messages is sent to a specific phone number, overwhelming the recipient's device and potentially rendering it unusable. The most likely scenario this occurs is when a user enters their phone number in a contact form or is trying to log in using an OTP. Hackers use this technique to frustrate the user and make them take a desired action which will make them vulnerable.
Malware attacks
SMS messages can be used to deliver malware to mobile devices. Attackers may send links to malicious websites or apps that install malware on the victim's phone, compromising its security.
Data leaks
Inadequate security measures on mobile devices or SMS gateways can lead to data leaks, where sensitive information contained in SMS messages is exposed to unauthorized parties.
Despite the vulnerabilities and lack of encryption, SMS is still the most preferred channel when it comes to 2FA. The reason is that the mobile carriers manage SMS messages have a secure infrastructure which compensates for the lack of encryption. Before going into the benefits of using SMS for 2FA, let’s do a quick refresher on how SMS authentication works.
How SMS authentication works
SMS authentication is a commonly used method to verifying a user’s identity. It works by sending a unique code or one-time password (OTP) via SMS to the user's registered mobile number. The user then enters the received code to confirm their identity and gain access to a service or account.
Benefits of SMS authentication
SMS authentication offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for enhancing security:
Enhanced security measures
SMS authentication adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts or services. Even if a password is compromised, the attacker would still need access to the user's mobile device to complete the authentication process.
User convenience
SMS authentication provides a convenient and user-friendly experience. Users don't need to remember complex passwords or carry additional hardware tokens. They can simply use their mobile device, which they already carry with them, to receive and enter the authentication code.
Wider accessibility
SMS is widely accessible, as most people own a mobile phone capable of receiving text messages. This makes SMS authentication suitable for a broad range of users, including those who may not have access to smartphones or internet connectivity.
Encryption and secure networks
To mitigate SMS security risks, it's crucial for mobile carriers to implement encryption and secure network practices. Telecom companies to should closely monitor incidents involving SMS interception, spoofing, and SMS flooding to identify potential vulnerabilities and fix them periodically to keep the infrastructure safe and reliable.
SMS security alerts and notifications
SMS can also be leveraged for security alerts and notifications. Organizations can send real-time SMS alerts to users informing them about suspicious activities, login attempts, or account changes. These alerts enable users to take prompt action and mitigate potential security breaches.
SMS notifications can also be used to keep users informed about important security updates, password reset instructions, and other critical service updates. By providing timely and relevant information via SMS, organizations can enhance user awareness and encourage proactive security measures.
How secure is SMS?
Every communication channel has its own vulnerabilities. SMS is no exception. But it serves as a relatively secure communication channel when used with other security measures.
Therefore, it's crucial to implement a multi-layered security approach that combines SMS with other security measures, such as encryption, Captcha, and other types of background security measures.

6 Potentials ways you can use SMS to strengthen your security
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Implement SMS-based 2FA to add an extra layer of security to user logins. Users receive an SMS with a unique code that they must enter along with their username and password to access their accounts.
- Account alerts: Use SMS to send real-time alerts to users about suspicious account activities, such as unusual login attempts or changes to account settings. This allows users to take immediate action if their account is compromised.
- Secure password reset: Employ SMS to securely reset user passwords. Instead of sending password reset links via email, which can be intercepted, send a temporary password or reset code via SMS to the user's registered mobile number.
- Transaction verification: For sensitive transactions, such as financial transfers or online purchases, use SMS to verify the user's identity and confirm the transaction details. This helps prevent unauthorized transactions and protects users from fraud.
- Critical information updates: Utilize SMS to send critical security information and updates to users, such as notifications about system maintenance, security patches, or data breach incidents. SMS ensures that users receive important information in a timely manner.
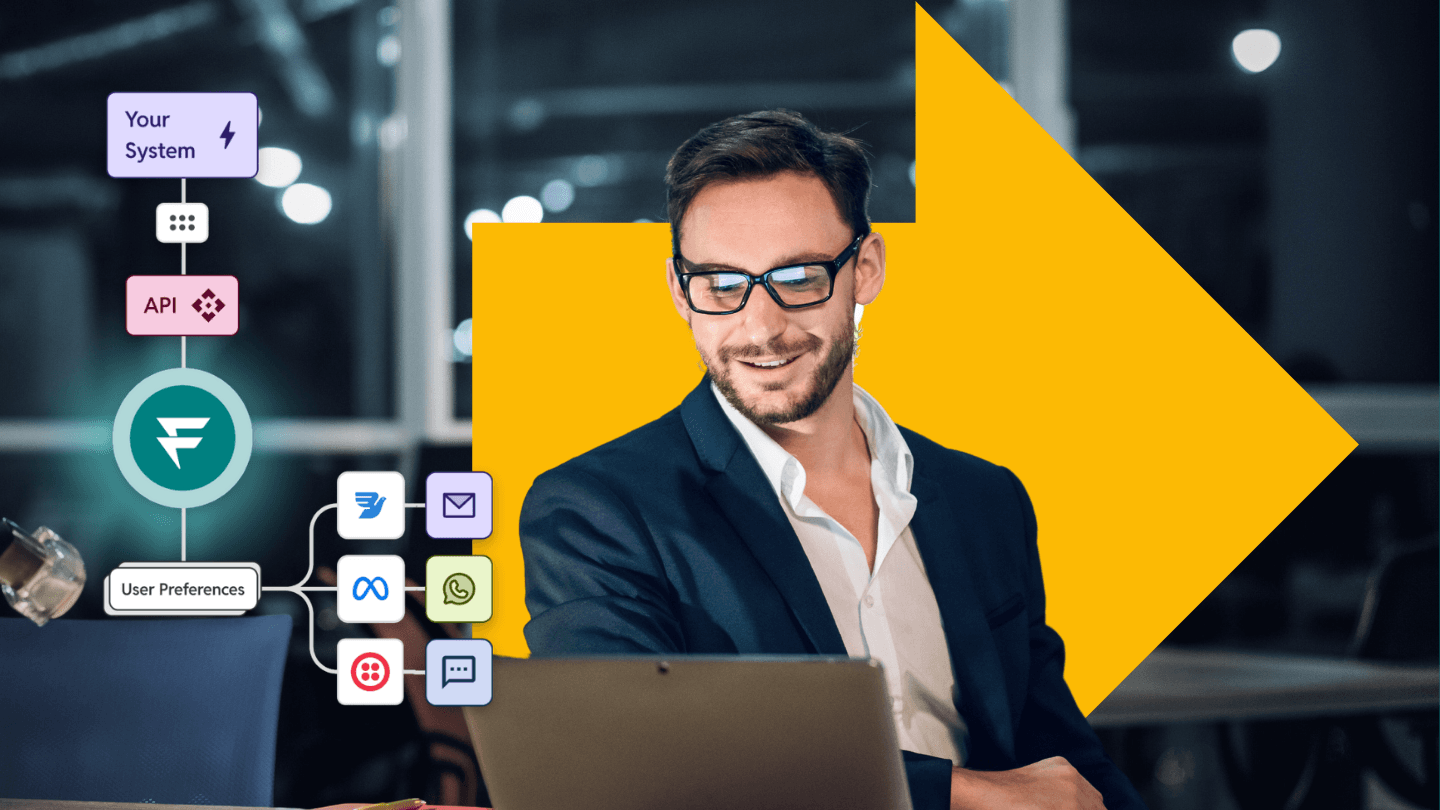
Fyno's role in SMS security
Fyno’s robust infrastructure platform can help you safely deliver SMS messages to your users without compromising on security and performance.
1. Opti-channel routing
Fyno's opti-channel routing allows businesses to intelligently route SMS messages based on various scenarios.
Opti-channel routing allows you to set up failover protocols in case of SMS delivery failure. You can add multiple SMS providers to the same workflow, setting up a condition to switch between providers in case of delivery failure. You can also set up workflows to use different mobile carriers to send SMS based on the Geography of the customer.
2. Hide sensitive user data
Fyno allows you to safeguard sensitive user data with the help of techniques like Masking.
Masking conceals sensitive information by replacing them with a “X” when displayed in the SMS as well as within the system.
For example, a phone number like “1234567890” would appear as “xxx-xxx-7890”, hiding the first six digits while still providing context. This allows you to share only the necessary information over SMS, while protecting all the other user information from unauthorized access.
3. Real-time alerts and monitoring
Fyno offers real-time alerts and monitoring capabilities to quickly detect and respond to SMS security threats. With continuous monitoring of SMS traffic, deliverability rates, and anomaly detection, Fyno can notify you about suspicious activities such as SMS flooding and offer you insights to take prompt action.
4. Compliance with regulatory standards
Fyno allows you to adhere to compliance and regulatory standards set for SMS communication. In India, TRAI has introduced the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) system to tackle the issue of unwanted commercial messages and spam SMS.
Fyno simplifies the DLT compliance process by providing a simple, user-friendly platform for businesses to manage their DLT requirements efficiently.
With Fyno, users can create, register, and manage all their DLT templates in one centralized location. The platform also enables the submission and approval of templates from various telecom operators.
By streamlining the DLT compliance process, Fyno saves businesses time and resources while helping them maintain transparency, protect customer privacy, and build trust with their audience.
Conclusion
SMS security is a critical aspect of 2FA authentication, and it shouldn’t be overlooked. While SMS offers convenience and accessibility, it also comes with inherent security risks and vulnerabilities. By understanding these risks, implementing appropriate security measures, and using state-of-the-art notification infrastructure like Fyno, businesses can protect their users' data.
FAQs
1. What is SMS security?
SMS security refers to the protection of SMS messages from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
2. Why is SMS important for 2FA?
SMS is widely used for two-factor authentication (2FA) due to its simplicity and broad accessibility.
3. What are common SMS security risks?
Common risks include SMS spoofing, interception, phishing (SMiShing), flooding, malware attacks, and data leaks.
4. How does SMS spoofing work?
SMS spoofing involves sending messages that appear to come from a trusted source to deceive recipients.
5. What is SMS interception?
SMS interception involves unauthorized access to SMS messages, often to steal sensitive data.
6. How can I protect against SMS phishing (SMiShing)?
Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources and verify the sender's legitimacy.
7. How does SMS authentication work and what are its benefits ?
SMS authentication sends a one-time code to a user’s phone, which they enter to verify their identity. Benefits include enhanced security, user convenience, and wide accessibility.