Every second, businesses worldwide send millions of SMS messages, whether for transactional updates, promotional offers, or customer service interactions. Yet, 74% of consumers now expect richer, more interactive experiences from these communications, leaving the humble SMS struggling to keep up.
Enter Rich Communication Services (RCS), a next-generation messaging protocol designed to bridge the gap between outdated SMS and the interactivity of modern messaging apps.
RCS doesn’t just deliver text; it transforms how businesses communicate. With capabilities like high-resolution media, interactive buttons, and real-time read receipts, RCS enables a seamless, app-like experience, all within a device’s native messaging app. Especially, for industries like banking, financial services, and logistics, these features are game-changers.
But why is RCS adoption gaining momentum now? The global Rich Communication Services (RCS) market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 24% from 2024 to 2032. With these numbers, it’s clear this isn’t just a passing trend, it’s the future.
In this article, we’ll uncover:
- What RCS is and how it enhances traditional messaging
- Industry-specific use cases that prove its value
- The technical and infrastructure readiness needed for seamless adoption
Whether you’re looking to improve compliance or simply stay ahead of the curve, RCS could be the tool your organization needs to transform customer interactions.
Let’s dive in.
1. Understanding Rich Communication Services (RCS)
1.1 What is RCS?
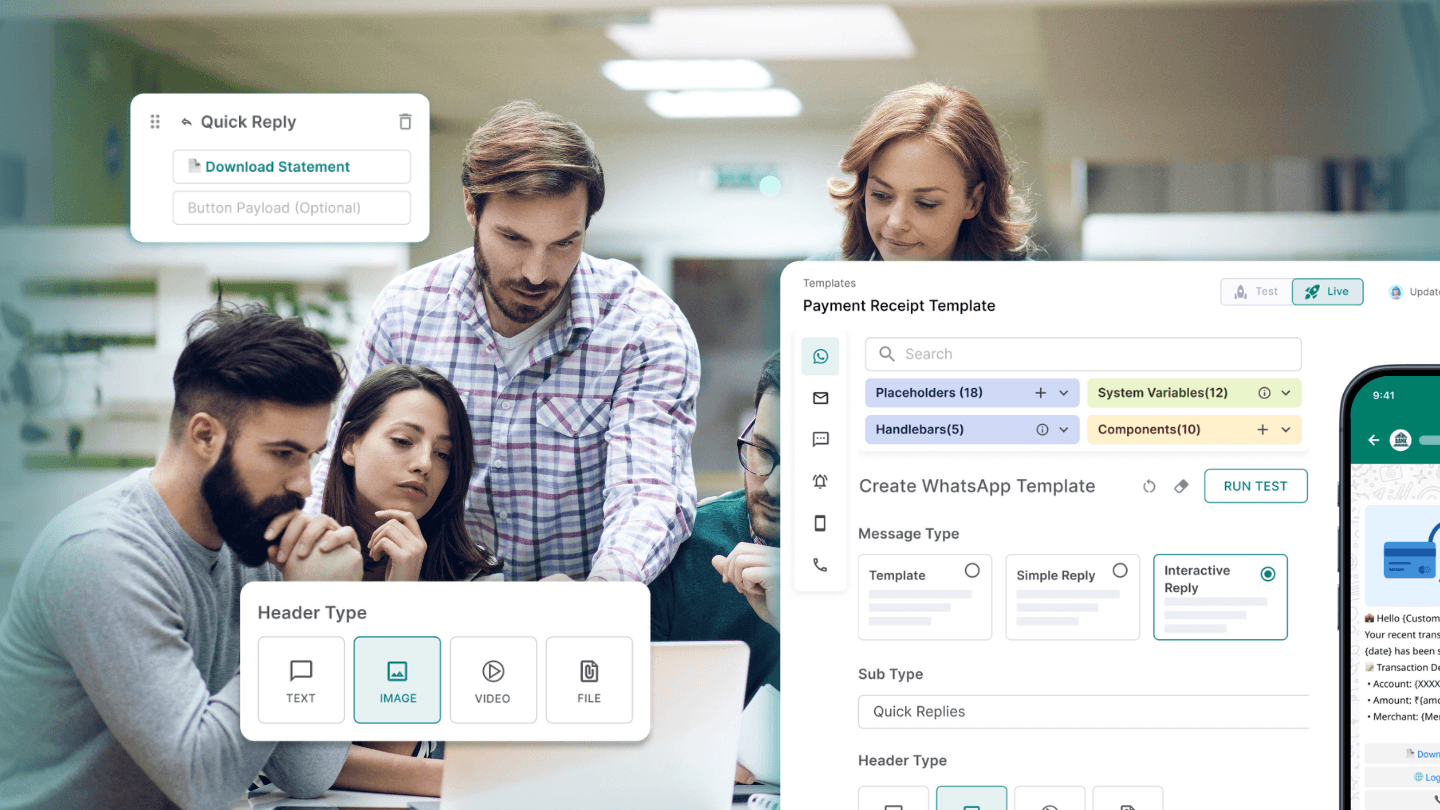
RCS is an advanced messaging protocol that enhances traditional SMS by incorporating features such as high-resolution images, videos, location sharing, and interactive buttons. It operates within the native messaging apps of devices, providing a seamless and secure user experience without the need for additional applications.
1.2 RCS in Banking, Financial Services, and Logistics
- Banking and Financial Services: RCS supports secure and compliant communications, including transaction notifications, fraud alerts, and customer service interactions. Its integration ensures adherence to financial regulations and enhances customer trust.
- Logistics: RCS facilitates real-time updates on shipment status, delivery scheduling, and customer feedback collection, streamlining operations and improving customer satisfaction.
Adoption Trends: The adoption of RCS is accelerating, with a reported 40% increase in business messaging adoption as of June 2023 compared to the previous year.
Actionable Insight: Evaluate your current communication channels to determine how RCS can enhance security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
2. Industry-Specific Use Cases
2.1 Banking and Financial Services
- Secure Transaction Alerts: Deliver encrypted transaction notifications with interactive options for customers to confirm or report suspicious activities.
- Regulatory Compliance Communications: Send policy updates and compliance notifications with read receipts to ensure customer acknowledgment, aiding in audit trails.
2.2 Logistics
- Real-Time Shipment Tracking: Provide customers with interactive messages containing live tracking information and options to reschedule deliveries.
- Proof of Delivery: Send images or signatures as proof of delivery directly through RCS, ensuring transparency and reducing disputes.
3. Core Infrastructure Readiness
Adopting Rich Communication Services (RCS) requires more than just enabling a new channel. For sectors like banking, financial services, and logistics, where reliability, compliance, and scalability are critical, infrastructure readiness is the cornerstone of successful RCS implementation. This section outlines the challenges, opportunities, and technical best practices to ensure your enterprise is RCS-ready.
3.1 The Complexity of Channel Integration
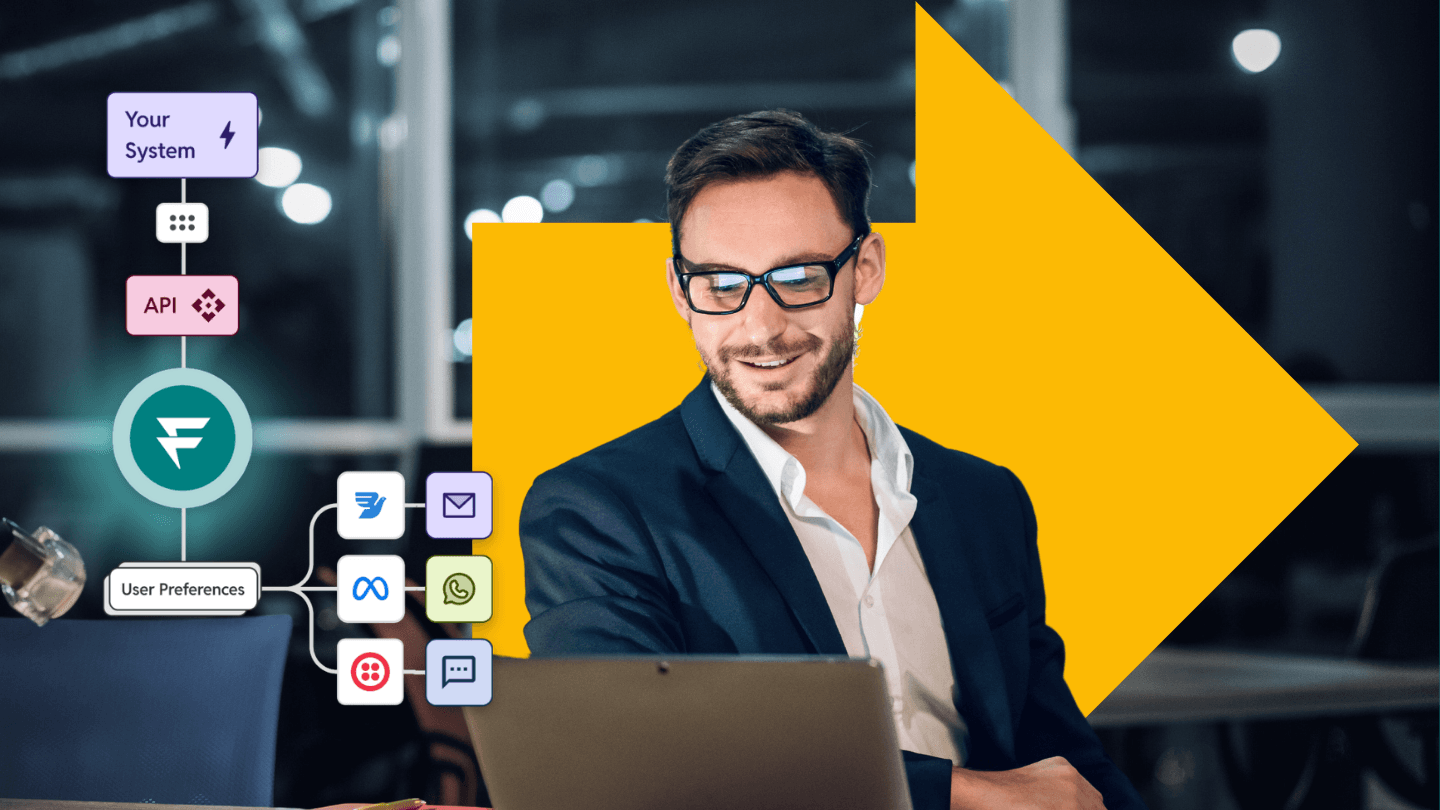
Modern enterprises often communicate with customers through multiple channels: SMS, email, app notifications, and now RCS. However, these channels are often siloed, leading to inefficiencies, increased costs, and gaps in compliance oversight. While these capabilities enhance communication, they also require:
- Unified APIs: To reduce the complexity of managing multiple channels.
- Infrastructure Adaptability: To handle rich media payloads and device-specific compatibility.
- Fallback Mechanisms: To ensure delivery when RCS is unsupported by devices or carriers.
Key Technical Challenges
- Fragmented Systems: Siloed APIs for SMS, email, and RCS lead to duplicated logic and inconsistent data synchronization.
- Bandwidth and Rich Media: RCS payloads, such as images and videos, consume significantly more bandwidth than SMS. Without infrastructure upgrades, enterprises risk delivery delays or service degradation during high-traffic periods.
- Dynamic Content Adaptation: Not all devices or networks can handle the same content formats. Enterprises must optimize message payloads dynamically for compatibility with different device capabilities.
Best Practices for Seamless Integration
- Consolidate APIs into a Unified Platform:
- Reduce complexity by adopting a messaging platform that supports multi-channel communication, including RCS, SMS, and email.
- Benefit: Simplifies compliance tracking and provides a unified analytics dashboard.
- Build Fallback Systems for Non-RCS Devices:
- Implement workflows that automatically switch to SMS or email when RCS is unsupported.
- Example: A delivery confirmation sent as an RCS message to compatible devices and as an SMS fallback for others.
- Optimize Media Delivery:
- Use adaptive content delivery systems that adjust media quality based on device capabilities and network conditions.
- Example: Sending a compressed image to low-bandwidth users while delivering full-resolution media to high-bandwidth users.
3.2 Designing for Scalability and Resilience
As enterprises adopt RCS, message volumes are expected to rise, particularly during high-demand scenarios like promotional campaigns or real-time alerts. A scalable infrastructure is essential to handle this growth while maintaining consistent performance.
- Peak Traffic Scenarios: Banking notifications (e.g., end-of-month statements) or logistics updates (e.g., holiday shipments) often cause traffic surges that legacy systems may not handle efficiently.
- Real-Time Expectations: Customers expect instant delivery of messages, especially for time-sensitive alerts like fraud notifications or shipment tracking. Delays can erode trust and, in regulated industries, result in compliance penalties.
Core Components of a Scalable System
- Elastic Cloud Infrastructure: Deploy messaging systems on platforms that can scale dynamically based on demand, such as Kubernetes clusters or cloud-based services.
- Message Queueing Systems: Use asynchronous message brokers like RabbitMQ or Kafka to decouple message production from delivery.
Benefit: Prevents bottlenecks during high-traffic periods.
- Intelligent Load Balancing: Distribute traffic across geographically distributed servers using load balancers.
Example: Geo-aware routing ensures users receive messages from the nearest server, reducing latency.
Ensuring Resilience and Redundancy
- Redundant Infrastructure: Set up duplicate systems in multiple regions to ensure uptime in case of localized failures.
- Message Retry Mechanisms: Implement logic to retry undelivered messages automatically, with exponential backoff to avoid overwhelming the system.
- Disaster Recovery Protocols: Maintain a well-documented disaster recovery plan, including regular drills to ensure operational continuity.
3.3 Embedding Compliance and Security
For regulated industries, security and compliance are non-negotiable. Adopting RCS introduces new data handling challenges, particularly with the transmission of sensitive information like OTPs, transaction notifications, or customer records.
- Data Localization Requirements: Some regulations (e.g., GDPR in Europe, India’s Data Protection Bill) mandate that customer data must remain within specific regions. RCS systems must ensure compliance with these rules.
- Auditability: All message transactions must be logged for regulatory audits. Enterprises must track:
- Message content and metadata.
- Delivery receipts and user interactions.
- Opt-In Mechanisms: Regulations require explicit customer consent before sending messages. Enterprises must implement robust opt-in and opt-out systems.
Security Best Practices
- End-to-End Encryption: Ensure encryption in messages in transit and at rest to prevent interception and tampering.
- Secure API Gateways: Use APIs with strong authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct penetration tests and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate security gaps.
3.4 Planning Transactional Communications Through RCS
Transactional messages such as password reset requests, account alerts, and delivery notifications are critical touchpoints that can benefit from RCS's rich features.
- Message Prioritization: Identify which transactional communications will benefit most from RCS's capabilities, such as two-factor authentication prompts or payment confirmations.
- Content Enhancement: Enhance messages with rich media and interactive elements to provide clear instructions and improve user engagement.
- Timeliness and Reliability: Ensure that RCS messages are delivered promptly and reliably, especially for time-sensitive communications like fraud alerts.
How can you do it?
- Audit Existing Communications: Review current transactional messages to determine suitability for RCS enhancement.
- Develop Templates: Create RCS message templates that incorporate rich media and interactive features for various transactional scenarios.
- Implement Testing Protocols: Conduct thorough testing to ensure messages render correctly across different devices and platforms.
3.5 Personalizing Messages Using Customer Data
Utilizing customer data to tailor messages can significantly increase relevance and adoption.
- Data Collection: Gather customer preferences, behaviors, and demographics to inform personalization strategies.
- Segmentation: Divide the customer base into segments based on shared characteristics to deliver targeted messages.
- Dynamic Content: Use dynamic content that adapts to individual customer data, such as personalized greetings or recommendations.
Actionable Steps:
- Implement Data Management Tools: Utilize customer data platforms (CDPs) to centralize and manage customer information.
- Develop Personalization Algorithms: Create algorithms that analyze customer data to generate personalized content.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly assess the effectiveness of personalized messages and refine strategies based on performance metrics.
3.6 Performance analysis and metrics
RCS offers advanced features that enable the collection of detailed engagement data, essential for assessing the effectiveness of messaging campaigns.
- Message Delivery Rate: The percentage of sent messages successfully delivered to recipients. This helps in identifying potential issues in the delivery process, such as network failures or incorrect contact information.
- Read Receipts: The number of messages opened by recipients.
- Interaction Rates: The frequency of user interactions with message elements, such as clicking on buttons or links.
- Conversion Rates: The proportion of recipients who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
3.7 Comparative Analysis: RCS vs. SMS Messaging Costs
RCS offers features like high-resolution images, videos, and interactive buttons, which can lead to increased customer engagement. However, these enhancements come with different cost structures compared to SMS.
- Per-Message Pricing: SMS typically ranges from $0.01 to $0.05 per message, depending on volume and provider agreements. While RCS approximately costs $0.055 per message in the U.S., though rates vary based on factors like message volume and network provider.
- Rich Media Content: Developing rich media content (e.g., images, videos) incurs additional expenses beyond basic text messages. RCS messages utilize data networks, potentially impacting costs related to data consumption.
Conclusion
Now here’s the million dollar question again: Is your organization RCS ready?
Adopting RCS is more than just a messaging upgrade—it’s a strategic shift that requires thoughtful planning and robust infrastructure.
This guide has provided a detailed roadmap to evaluate your organization’s readiness across key areas:
- Infrastructure Readiness: Ensuring seamless channel integration, scalability, and reliability.
- Compliance and Security: Adhering to industry regulations and safeguarding sensitive data.
- Cost and ROI Analysis: Balancing direct and indirect costs with potential revenue growth.
By addressing these aspects, enterprises in banking, financial services, and logistics can leverage RCS to enhance operational efficiency, meet regulatory requirements, and deliver rich customer experiences.
To make things easy, and to help you assess your RCS readiness, we've create a detailed readiness checklist for RCS. You can download it from here.
If you wish to know more how Fyno can help you streamline your communication strategy, especially around RCS, talk to us.