Navigating HIPAA compliance data breach: Understanding notification rules
In the healthcare sector, safeguarding patient data is not just a legal obligation but a moral one. That’s why the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates stringent measures to protect patient information.
One critical aspect of HIPAA, which we’ll be focusing on, is the Breach Notification Rule. The event of a data breach requires HIPAA covered entities to notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and sometimes the media, depending on the extent of the breach.
Thus, understanding how to handle a data breach is essential for ensuring compliance and maintaining patient trust.
In this blog post, we will cover everything related to HIPAA breaches, from common scenarios that contribute to their occurrence to handling them effectively and restoring patient trust.
Let’s get started.

Defining a HIPAA breach
A HIPAA breach occurs when the unauthorized use or disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI) compromises the security or privacy of patients. A covered entity has specific duties under HIPAA regulations, including risk analysis, breach notification, and compliance.
Not all incidents qualify as breaches under HIPAA.
For example, unintentional access by an authorized employee or inadvertent disclosure to another authorized individual within the same organization may not be considered a breach if the information is not further used or disclosed improperly.
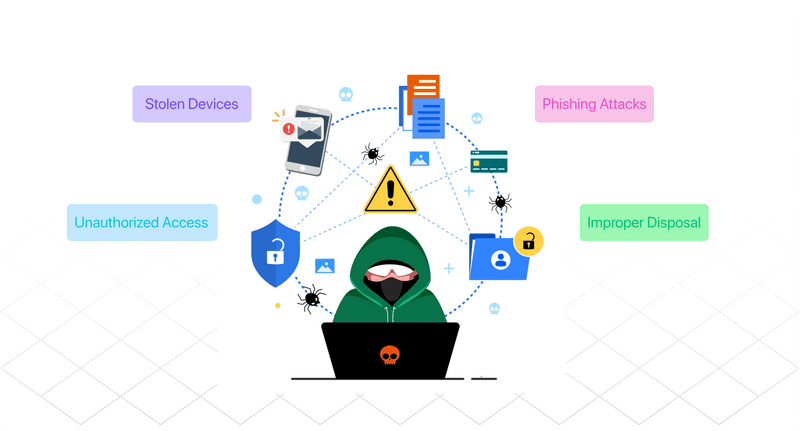
Examples of common breaches and scenarios in healthcare data
- Lost or stolen devices: If lost or stolen, mobile phones, laptops, or USB drives containing unencrypted PHI can lead to significant breaches.
- Unauthorized access: Instances where employees access patient records without a legitimate reason. Business associates must also ensure that their employees do not access patient records without a legitimate reason.
- Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals trick employees into revealing sensitive information through deceptive emails.
- Improper disposal: Discarding paper records or electronic devices containing PHI without proper destruction.
Key requirements of HIPAA breach notification
Once a breach is detected, healthcare entities must act immediately to comply with HIPAA’s notification requirements. The HIPAA Security Rule outlines the safeguards that must be in place to protect electronic PHI. Compliance with HIPAA rules is essential for avoiding penalties.
Here are the key steps and timelines involved:
Immediate steps after breach detection
- Contain the breach: Immediately contain the breach to prevent further unauthorized access or disclosure of patient information. Covered entities must act quickly to contain the breach and prevent further unauthorized access.
- Conduct a risk assessment: Evaluate the nature and extent of the breach, the root cause of the breach, and the person involved. Also, try to get as much information as possible on the data used. This includes gathering information on who viewed the data, who it was sent to, and what purposes it was used for, etc.
Notification timelines and procedures
After containing the breach and doing a root cause analysis, the next critical step is to notify the affected and the authorities about the breach. Here are the timelines mentioned in the HIPAA guidelines.
- Individuals: The affected institution should notify affected individuals without unreasonable delay and no later than 60 days after discovering the breach. Notifications should include a description of the breach, the types of information involved, steps individuals can take to protect themselves, and what the entity is doing to investigate and mitigate the breach.
- Department of Health and Human Services (HHS): If the breach impacts 500 or more individuals, the affected institution should notify the HHS within 60 days. For breaches affecting fewer than 500 individuals, the institution must maintain them on record internally and report them to HHS annually.
- Media: If the breach affects more than 500 residents of a state or jurisdiction, the affected institution must notify prominent media outlets in the area within 60 days.
Additionally, HIPAA data breach notification requirements must be followed to ensure compliance with federal and state laws.
Special considerations for notifications to individuals and authorities
- Contact information: If the individual has agreed to electronic communication, use first-class mail or email. If contact details are insufficient, use alternative methods like phone or public postings on the entity’s website.
- Content of notices: Ensure notifications are clear and include all necessary information to help affected individuals understand the breach and protect themselves.
Penalties and consequences for non-compliance
Non-compliance with the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule can result in severe penalties. The penalty can range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million.
Failing to protect unsecured protected health information can result in severe penalties for covered entities and business associates.
Case studies of recent HIPAA breach penalties
Here are two notable case studies that illustrate the severe consequences of failing to adhere to HIPAA guidelines adequately.
Anthem Inc.
In 2015, Anthem Inc., one of the largest health benefits companies in the United States, experienced a massive data breach that impacted nearly 79 million individuals.
The breach exposed sensitive information, including names, social security numbers, medical identification numbers, and other personal data. This incident occurred due to a sophisticated cyber-attack where hackers accessed Anthem's IT system through phishing emails sent to employees.
The repercussions were significant.
Anthem agreed to a record-setting settlement of $16 million with the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Additionally, Anthem was required to implement a corrective action plan to address deficiencies in its HIPAA compliance program.
Premera Blue Cross
In 2019, Premera Blue Cross, a health insurance provider, faced a substantial penalty following a data breach that exposed the sensitive personal information of over 10 million individuals.
The breach, which was discovered in 2015 but had begun in 2014, involved unauthorized access to Premera’s IT systems. The attackers accessed sensitive information, including social security numbers, bank account information, and clinical data.
Premera Blue Cross settled with the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) for $10 million. The organization was also required to adopt a comprehensive corrective action plan to enhance its data security practices.
These case studies illustrate the severe financial and operational impacts of HIPAA breaches. By learning from these examples, organizations can better prepare to protect patient information and avoid similar pitfalls.
Compliance best practices
Importance of staff training on HIPAA breach reporting
Regular training programs are essential to educate employees about HIPAA regulations, how to identify potential breaches, and the steps to take when a breach occurs.
Staff should be well-versed in the organization’s policies and procedures related to data security and breach notification.
Implementing robust data security measures
- Access controls: Implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- SOP for disposal of computer hardware: Healthcare institutions should devise and follow standard procedures to dispose of any non-functional hard disks or devices containing sensitive patient information.
- Well-structured exit procedures: Establish standard exit procedures to prevent ex-employees from accessing sensitive information from outside. This involves restricting their access to email and other internal services.
- Encryption: Encrypt all PHI at rest and in transit to protect against unauthorized access. This can be effectively implemented with the help of your internal IT team or by getting expert help from outside.
- Regular audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. If you detect a breach during the audit that went unnoticed, immediately follow protocol. Contain the breach and report it to the respective authorities and patients within the timeline set by HIPAA.
How fyno supports robust data security practices
As a leading notification infrastructure platform, Fyno offers several features to help healthcare institutions enhance their data security practices and comply with HIPAA regulations.
Fyno's features help protect individually identifiable health information from unauthorized access.
Features that protect customer data
1. Universal integration layer: Having copies of your patient records on multiple customer data platforms (CDPs), say one for automation, another for routing etc., increases your chance of a breach.
Instead, you could use one dedicated CDP for all use-cases to manage these information. With Fyno, you can integrate and manage all your communication channels from one central location. This ensures secure and consistent data handling across platforms.
2. Logical orchestration layer: Our powerful cross-channel workflow orchestration layer minimizes the need for human intervention, leading to limited access to patient information.
Enhancing data integrity and confidentiality
- Data encryption: Fyno ensures that all data, including PHI, is encrypted to prevent unauthorized access with one-way hashing.
- Access management: Role-based access control and single sign-on (SSO) features ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Fraud prevention: Fyno’s fraud detection mechanisms help identify and mitigate potential security threats, ensuring compliance with HIPAA’s stringent requirements.
Effectively adhere to HIPAA compliance with fyno
Navigating HIPAA compliance, particularly the Breach Notification Rule is crucial for healthcare entities to protect patient information and avoid hefty penalties.
Organizations can safeguard PHI and maintain patient trust by understanding the requirements and implementing robust data security measures. Platforms like Fyno provide the tools to streamline communication, enhance data security, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Embrace these best practices and leverage advanced solutions to effectively navigate the complexities of HIPAA compliance.
FAQs
1. What constitutes a HIPAA breach?
A HIPAA breach involves the unauthorized use or disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI).
2. How soon must individuals be notified after discovering a HIPAA breach?
Individuals must be notified without unreasonable delay and no later than 60 days after discovering the breach.
3. What information should be included in a breach notification to affected individuals?
Notifications should describe the breach, types of information involved, steps to protect themselves, and what is being done to mitigate the breach.
4. When must the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) be notified of a HIPAA breach?
HHS must be notified within 60 days for breaches affecting 500 or more individuals; annually for breaches affecting fewer than 500 individuals.
5. Under what circumstances must the media be notified of a HIPAA breach?
The media must be notified if the breach affects more than 500 residents of a state or jurisdiction.
6. What are the penalties for non-compliance with HIPAA Breach Notification Rules?
Penalties range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million.
7. What is the role of risk assessment after a HIPAA breach?
A risk assessment evaluates the nature and extent of the breach, including the types of PHI involved and the potential impact on individuals.
8. How can healthcare entities prevent HIPAA breaches?
Implementing robust data security measures such as encryption, access controls, regular audits, and staff training can help prevent breaches.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted