What is SMS spoofing?
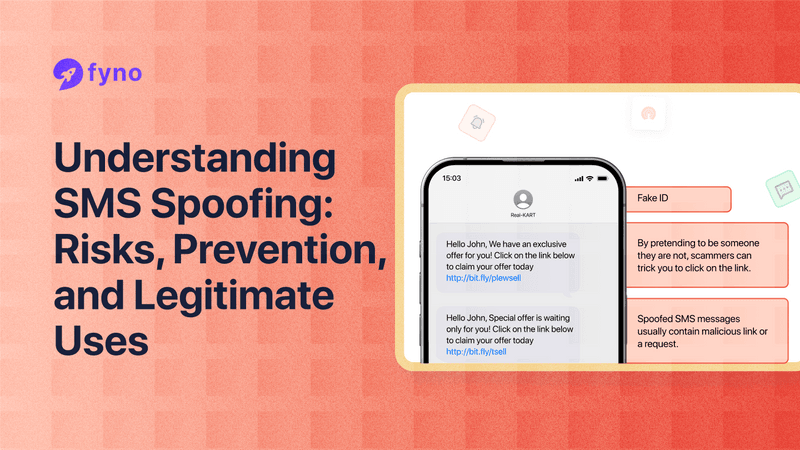
SMS spoofing involves sending text messages with a forged sender ID to make it appear that the message is from a trusted source. This technique is often used in scams and phishing attacks to trick recipients into divulging personal information or clicking on malicious links. Spoofed messages can look like they are from banks, government agencies, or even personal contacts, making them particularly deceptive
For instance, scammers might use SMS spoofing to send fake notifications about suspicious activities on bank accounts, urging recipients to respond immediately with sensitive information.
Difference between SMS spoofing and smishing
While SMS spoofing and smishing both involve deceitful text messages, there are distinct differences between the two. SMS spoofing focuses on altering the sender ID to mask the true origin of the message. This is done to gain the recipient's trust.
In contrast, smishing (SMS phishing) specifically refers to sending text messages that appear to be from legitimate entities to steal personal information or spread malware. Smishing often includes links to fake websites designed to capture user credentials.
Both tactics exploit the trust recipients place in familiar or authoritative sources but use slightly different methods to achieve their malicious goals.
How SMS spoofing works
SMS spoofing is a technique scammers use to send text messages that appear to come from a trusted source. They manipulate the sender ID of a text message to make it appear as if it was sent from a different phone number. This method allows scammers to trick recipients into believing the message is genuine, potentially leading to the disclosure of personal information or money transfers.
Technical explanation of SMS spoofing
Alteration of sender ID: Scammers use software or online services to change the sender ID of their messages. This process involves entering a different phone number or alphanumeric text as the sender ID.
Delivery process: The altered message is sent through an SMS gateway, which forwards it to the recipient's mobile network. The message appears to come from the spoofed sender.
Deception tactics: By mimicking legitimate sources, these messages often contain urgent requests or warnings to trick recipients into acting quickly, such as clicking a malicious link or providing sensitive information.
How spammers use fake sender IDs to deceive recipients
Phishing attacks: Spammers send messages that appear to come from trusted organizations, such as banks or service providers, asking for account details or personal information.
Spreading malware: Some spoofed messages contain links that, when clicked, install malware on the recipient's device. This malware can steal personal data or perform other malicious activities.
Fake money transfers: Scammers use fake sender IDs to request money transfers. For instance, a message might seem to come from a friend or family member urgently needing funds.
Bypassing spam filters: Spoofed SMS messages can sometimes bypass spam filters because they seem to come from a trusted source, increasing the chances of reaching the recipient's inbox.
Risks of SMS spoofing
Identifying fraudulent text messages is crucial, as spoofing attacks can lead to severe consequences, including identity theft and financial losses.
Types of SMS spoofing attacks
SMS spoofing can be especially harmful as it often bypasses spam filters, allowing fraudulent messages to reach their intended victims. Below are five types of SMS spoofing attacks.
Unsolicited bulk messages (UBMs)
Harassment
Fake money transfers
Corporate espionage
Identity theft
Let's look at each one of them in detail below.
1. Unsolicited bulk messages (UBMs)
Unsolicited Bulk Messages (UBMs) are often used in SMS spoofing to send numerous messages to numerous recipients. These messages typically contain advertisements or phishing links designed to steal personal information. Scammers rely on UBMs to spread their malicious content widely, increasing the chances of finding victims.
2. Harassment
Harassment through spoofed SMS messages involves sending threatening or abusive texts from a fake sender ID. This tactic intimidates and distresses the recipient, making it difficult to trace the sender. Harassment via spoofed texts can have severe emotional and psychological effects on the victim.
3. Fake money transfers
Fake money transfers are a common form of SMS spoofing, in which scammers send messages pretending to be from a bank or financial institution. These messages often instruct recipients to provide their bank account information or click on a malicious link. Victims of such attacks may lose significant amounts of money if they follow the instructions in the spoofed SMS.
4. Corporate espionage
Spoofing attacks are used in corporate espionage to gather sensitive information from businesses. Scammers might send messages that appear to come from within the company, requesting confidential data or access to secure systems. Such attacks can lead to significant financial and reputational damage for the targeted company.
5. Identity theft
Identity theft is a major risk associated with SMS spoofing. Scammers use spoofed messages to trick individuals into revealing personal information such as social security numbers, addresses, and bank details. This stolen information can then be used to commit fraud, apply for credit in the victim's name, or conduct other illegal activities.
Impact on businesses and individuals
Financial losses: Victims of SMS spoofing can experience significant financial losses due to unauthorized transactions or scams.
Reputation damage: Businesses affected by spoofing attacks may suffer from reputational harm, leading to a loss of customer trust.
Data breaches: Spoofed messages can lead to data breaches, exposing sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
Legal consequences: Companies failing to protect against SMS spoofing might face legal actions and penalties.
Operational disruptions: Spoofing attacks can disrupt normal business operations, causing delays and financial setbacks.
Identifying SMS spoofing
By recognizing the signs of spoofing, individuals can better protect themselves from these deceptive messages. Sending a spoof text message is illegal if used for malicious purposes or fraud, but it can be legal when organizations use their real name as the sender ID.
Spoof text messages can be challenging to identify, but knowing what to look for can help you avoid being a victim of these attacks.
Warning signs of SMS spoofing
The five warning signals for SMS spoofing attack are listed below.
Suspicious terminology
Unrecognisable phone number
Grammar and spelling mistakes
Strange URLs
Unclickable sender field
Let's look at each one of them now.
Suspicious terminology: Spoofed SMS messages often contain unfamiliar or suspicious terms. Look out for messages that include jargon or terms that seem out of place, as these can indicate a spoofing attempt. The message may appear urgent or alarming, prompting immediate action.
Unrecognisable phone number: A common sign of SMS spoofing is receiving messages from unrecognizable or unusual phone numbers. These numbers might be international or appear as a string of random digits. Legitimate messages usually come from recognized contacts or known service providers.
Grammar and spelling mistakes: Spoof text messages often have noticeable grammar and spelling mistakes. Scammers rely on the message's urgency to bypass thorough reading, but errors in the text can clearly indicate a spoofing attempt. Be wary of messages that do not follow standard language rules.
Strange URLs: Many spoofing messages contain strange or unfamiliar URLs. These links can lead to malicious websites that steal personal information or install malware on your device. Always hover over a link to check its legitimacy before clicking.
Unclickable sender field: In some spoofed messages, the sender's identity may appear as a name or company, but the field itself is unclickable. Legitimate messages usually allow you to interact with the sender's information. It may be a spoofed SMS if you cannot click or view more details about the sender.
Identifying these warning signs is crucial for preventing SMS spoofing attacks. By staying vigilant and informed, you can protect your personal information and avoid falling victim to scammers.
Protecting yourself from SMS spoofing
Protecting yourself from SMS spoofing is crucial to avoiding fraud and identity theft. Here are some essential steps to safeguard against spoofing attacks and maintain the security of your personal information.
Cybersecurity tips to prevent SMS spoofing
A few expert-provided tips to prevent SMS spoofing attacks are as follows.
Verify the sender
Beware of suspicious messages
Use two-factor authentication
Keep your phone number private
Use anti-spoofing technology
Now, let's get into the specifics of each one of them.
1. Verify the sender
Always verify the sender's identity before responding to any suspicious SMS message. Scammers use fake sender IDs to trick recipients into believing that messages are from legitimate sources. Contact the actual sender through official channels to confirm the message's authenticity.
2. Beware of suspicious messages
Be cautious of unsolicited bulk messages or texts containing spelling mistakes and suspicious links. These are common signs of SMS spoofing. Avoid clicking on any links or providing personal information through such messages, as they may lead to malware installation or identity theft.
3. Use two-factor authentication
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts to add an extra layer of security. 2FA requires a second form of verification, making it harder for scammers to gain access to your accounts even if they have your phone number.
4. Keep your phone number private
Limit sharing your phone number online and with untrusted sources. Scammers can use your phone number to send spoofed messages or commit fraud. Be mindful of where and with whom you share this sensitive information.
5. Use anti-spoofing technology
Install anti-spoofing software or apps that help detect and block spoofed SMS messages. These tools can identify fake sender IDs and prevent malicious texts from reaching your inbox. Regularly update your phone's settings and security software to stay protected.
Best practices for sending SMS messages
Sending SMS messages securely requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices.
First, use a trusted service provider that offers robust security features. Trusted providers help prevent SMS spoofing and ensure your messages are delivered accurately.
Second, implement strong authentication mechanisms. Two-factor authentication (2FA) can significantly reduce the risk of spoofing texts by verifying the sender's identity.
Third, security protocols should be regularly updated to stay ahead of new threats. Keeping your systems and software up-to-date minimizes vulnerabilities.
How businesses can ensure secure messaging
Businesses must take proactive steps to secure their messaging systems. Here are three critical practices:
Use trusted service providers
Implement strong authentication mechanisms
Regularly update security protocols
Let's look at each of them in detail one by one.
1. Use trusted service providers
Using trusted service providers is crucial in preventing SMS spoofing. These providers offer enhanced security features like encryption and two-factor authentication, which protect against spoof text messages. A trusted provider also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations, providing an additional layer of security.
2. Implement strong authentication mechanisms
Strong authentication mechanisms are essential in securing SMS communications. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a widely adopted method that adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a secondary device or code. This reduces the likelihood of spoofing SMS and ensures that only authorized users can send messages.
3. Regularly update security protocols
Regularly updating security protocols is vital for maintaining the integrity of your messaging systems. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and outdated protocols can leave systems vulnerable. Regular updates, including patches and software upgrades, help protect against new types of spoofing attacks and other security threats.
Legitimate uses of SMS spoofing
SMS spoofing is not always used for malicious purposes. Several legitimate applications use SMS spoofing to play a crucial role.
Bulk messaging services
Marketing campaigns: Companies use bulk messaging services to send promotional offers, updates, and advertisements. For instance, a retail chain might send discount coupons to its customers.
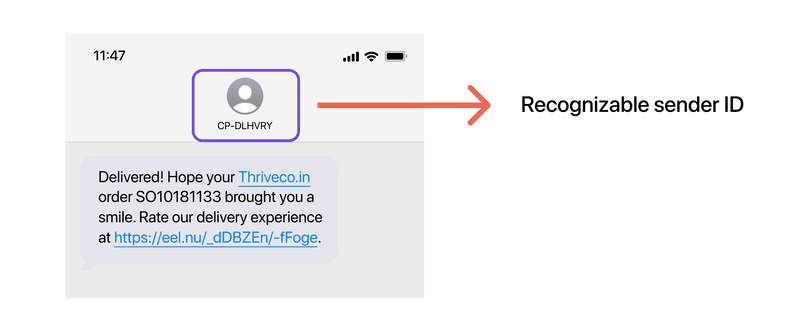
Customer notifications: Banks and logistics companies often send notifications regarding transactions, delivery statuses, and account activities. Using a recognizable sender ID ensures that the recipients trust and read the messages.
Official messages
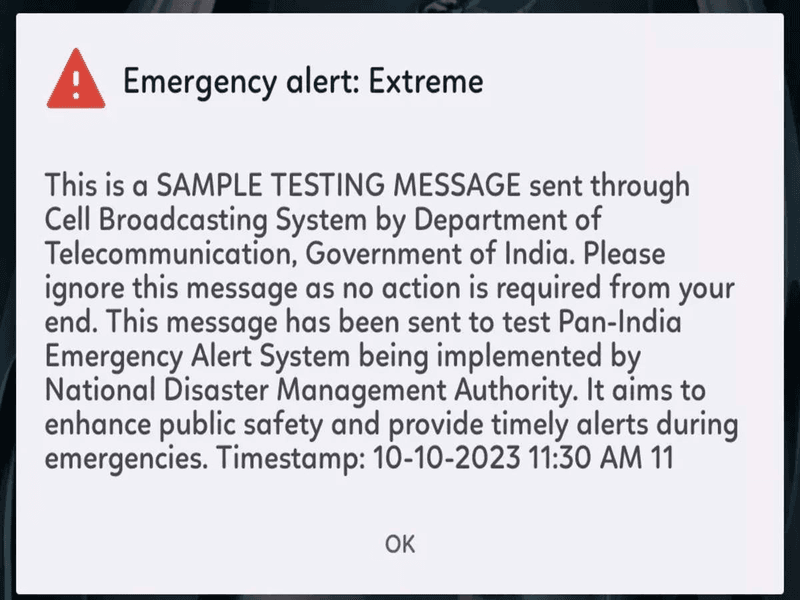
Government alerts: Governments use SMS spoofing to send emergency and important notifications. These messages often come from a trusted source, such as a government agency.
Healthcare reminders: Hospitals and clinics send patients appointment reminders and health alerts. These messages are crucial for ensuring that patients receive timely care.
Identity protection
Two-factor authentication (2FA): Many online services use spoofed SMS to send one-time passwords (OTPs) to users, adding an extra layer of security to online accounts.
Verification codes: Banks and financial institutions send verification codes to confirm transactions or changes in account settings. These codes help prevent unauthorized access and fraud.

How fyno can help prevent spoofing attacks
Fyno is committed to enhancing SMS security by implementing robust measures to prevent spoofing attacks. Spoofing attacks involve scammers sending fraudulent messages that appear to come from trusted sources. Fyno addresses this issue by securing sender credentials, ensuring Data Localization (DLT) details, and securely syncing DLT templates.
Securing senders' credentials
Authentication mechanisms: Fyno employs advanced authentication mechanisms to verify senders' identities. This ensures that only authorized users can send messages.
Encryption: All communication channels are encrypted, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Regular audits: Fyno conducts regular audits to identify and rectify any security vulnerabilities, ensuring ongoing protection against spoofing attempts.
Securing DLT details
Compliance: Fyno ensures compliance with all regulatory requirements for DLT, protecting against unauthorized access to DLT data.
Data integrity: Measures are in place to maintain the integrity of DLT data, ensuring that it cannot be tampered with by malicious actors.
Access control: Strict access control policies are enforced to ensure that only authorized personnel can access DLT details.
DLT templates sync
Secure fetching: Fyno securely fetches DLT templates, eliminating the need for file uploads and reducing the risk of spoofing. Say, for instance, this is possible with providers like Vodafone Idea Limited (VIL).
Template verification: All templates are verified before use, ensuring they comply with regulatory standards and preventing unauthorized modifications.
Automated updates: Fyno provides automated updates for DLT templates, ensuring that the latest templates are always in use and reducing the risk of outdated or compromised templates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SMS spoofing presents significant risks, such as identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized access to sensitive information. These risks can be mitigated by understanding scammers' methods and implementing preventive measures like verifying sender IDs, using anti-spoofing software, and educating employees.
Choosing reliable communication solutions enhances security, improves trust and credibility, ensures compliance with regulations, and maintains operational efficiency, especially in sectors like BFSI and logistics.
FAQs
1. What is SMS spoofing?
SMS spoofing involves sending text messages with a forged sender ID to make it appear that the message is from a trusted source.
2. How does SMS spoofing differ from smishing?
While SMS spoofing alters the sender ID to mask the true origin, smishing sends messages appearing to be from legitimate entities to steal personal information.
3. What are the main risks of SMS spoofing?
The main risks include identity theft, financial loss, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and spreading malware.
4. How can I identify an SMS spoofing attempt?
Warning signs include suspicious terminology, unrecognizable phone numbers, grammar and spelling mistakes, strange URLs, and unclickable sender fields.
5. What steps can I take to protect myself from SMS spoofing?
Verify the sender, beware of suspicious messages, use two-factor authentication, keep your phone number private, and use anti-spoofing technology.
6. Does SMS spoofing have legitimate uses?
Yes, legitimate uses include marketing campaigns, customer notifications, government alerts, healthcare reminders, and two-factor authentication.
7. How can businesses ensure secure messaging to prevent SMS spoofing?
Businesses should use trusted service providers, implement strong authentication mechanisms, and regularly update security protocols.