Security
Security is considered one of Fyno’s biggest selling points since we deal with the transmission of a lot of sensitive information and Personal Identifiable Information.
Therefore while implementing the Security features, a lot of consideration was put in, keeping Compliance as well as client data discretion in mind.
Fyno has 5 Security features that can be enabled for your account:
- Data Masking
- Data Payload Storage
- Approval Requests
- Secure Allowlist Endpoints
- Secure Media Storage
Before you enable any of these features, it is important to understand what each one does, to ensure your use case is being covered and you are achieving the security data protection.
Data Masking
Masking a piece of information means covering it. In the simplest of terms, masking is a 2-way feature that enables you to cover sensitive data points on the Fyno application when it’s being displayed.
When and How it Works?
Masking, when activated, will be implemented on the below 2 data points that we receive from you:
- Data Payload
- Destination
Fyno’s Masking feature works as below:
- Fyno receives an API request from your end with one or both of the above-mentioned data points.
- On receiving the API Request, if Masking is toggled on, then the data will be stored in the database as plain text format
- On viewing these data points on the Fyno application, they will be displayed in a masked format - xxxxx.
Enabling Masking
To enable the Masking feature for your account,
Once done, all your Data Payload and Destination details will be masked across the application. You can see this in the following places:
- Sent logs
- Notification Event Logs
- Workflow Logs
You will be able to see the masked data as a string of “xxxxx” where the sensitive information is supposed to be.
Data Payload Storage
You can decide whether you want to store the data payload you send to Fyno or not using this setting.
How it Works?
Data Payload storage, when activated, will be implemented on the below data point that we receive from you:
- Data Payload
- Payload sent to workflows.
Fyno’s Data Payload Storage feature works as below:
- Fyno receives an API request from your end with the data payload.
- On receiving the API Request, if Data Payload Storage is toggled on, then we will store the data payload at our end.
If its disabled, you won’t see any Placeholders data in the logs.
Enabling Data Payload Storage
To enable the Data Payload Storage feature for your account,
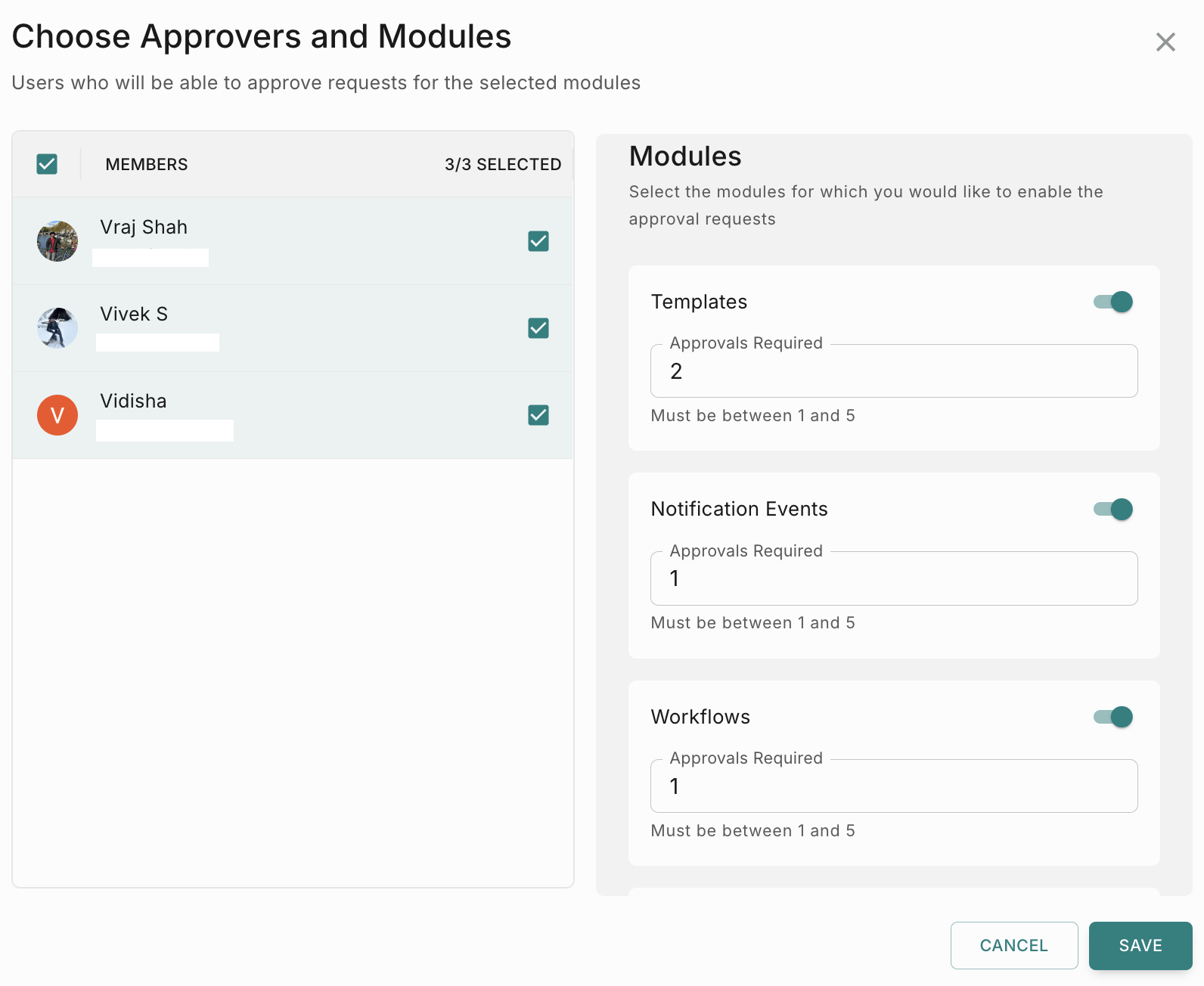
Approval
This feature will enable you to add a approval process when anyone promotes a feature from Test to Live. This additional step ensures to prevent incorrect or unintended communications from reaching users.
To enable Approval flow for Templates, Notification events and Workflows, follow the below steps.
Secure Allowlist Endpoints
This feature adds a security layer to verify that the API request originated from Fyno by generating Signature using HMAC key. You can leverage this feature when you call your APIs from workflows and also when you receive delivery reports from Fyno to your endpoint.
The signature will be included in the API request header as X-fyno-hmac-signature.
To enable the Secure Allowlist Endpoints feature for your account,
Fyno will use the secret key to encrypt the JSON payload (using SHA-256 algorithm) and create a signature and send it as part of the API request header. The customers can then decrypt using the Key to check if the payload remained intact and not corrupted.
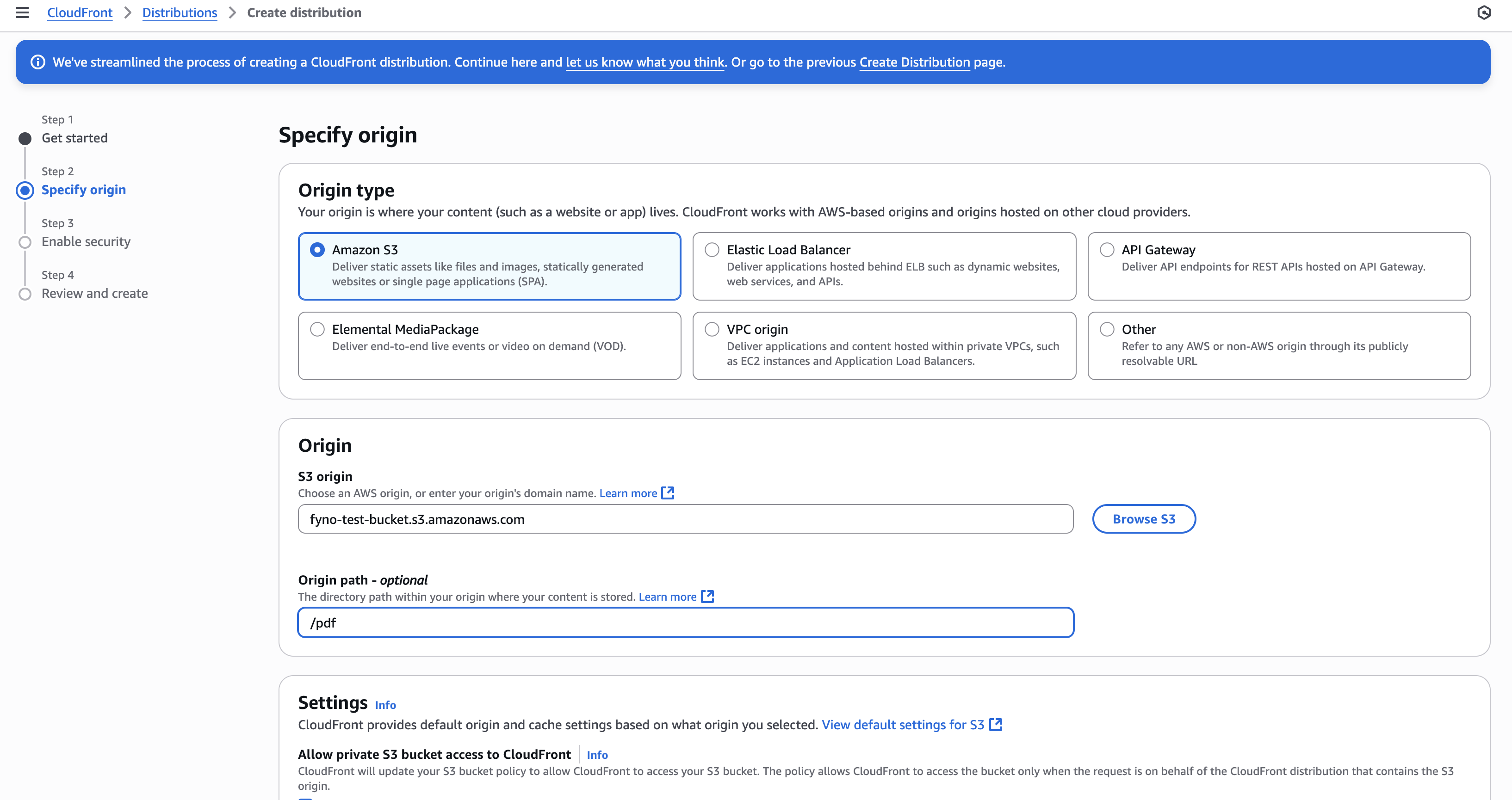
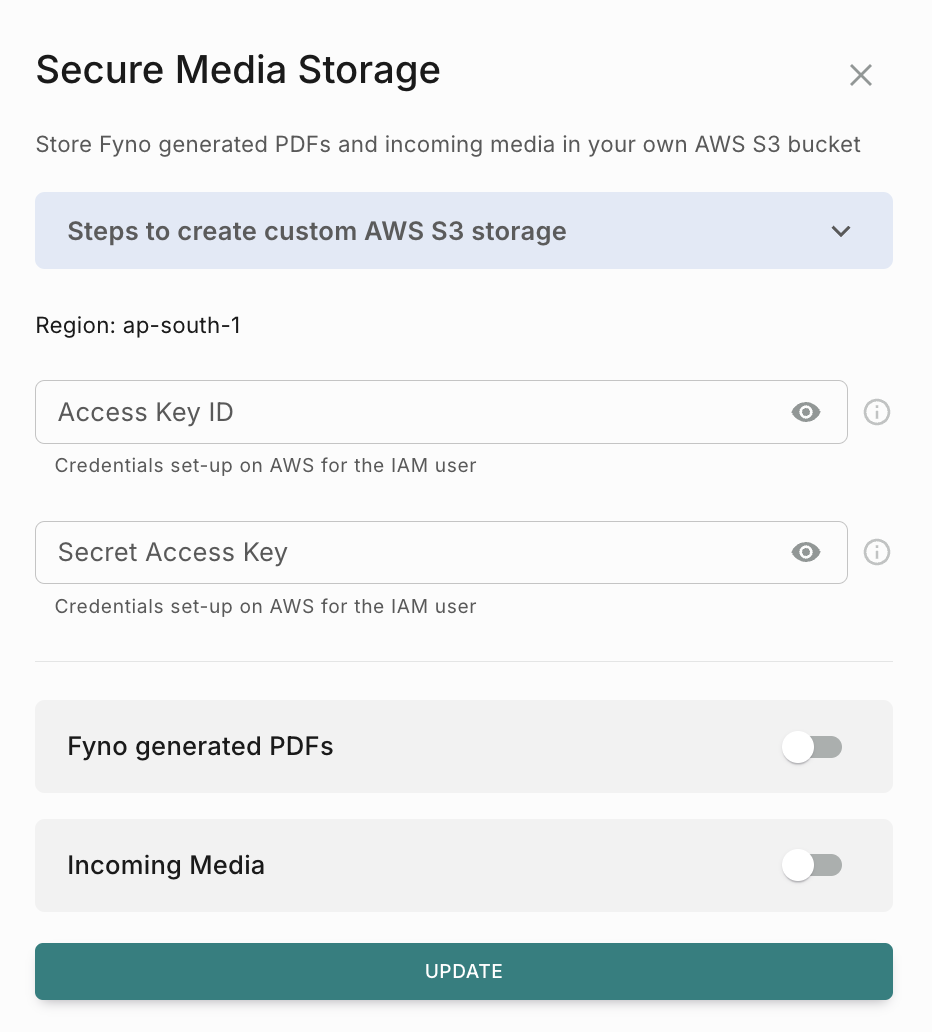
How to configure custom media storage
This feature enables you to store media files sent using Fyno’s PDF component or any incoming media (like jpeg, png, pdf etc) received from your customers via WhatsApp in your private S3 bucket to make sure all the media file are secure. ¸
The prerequisite for enabling secure media storage is to Create custom AWS S3 storage.
How to Create custom AWS S3 storage
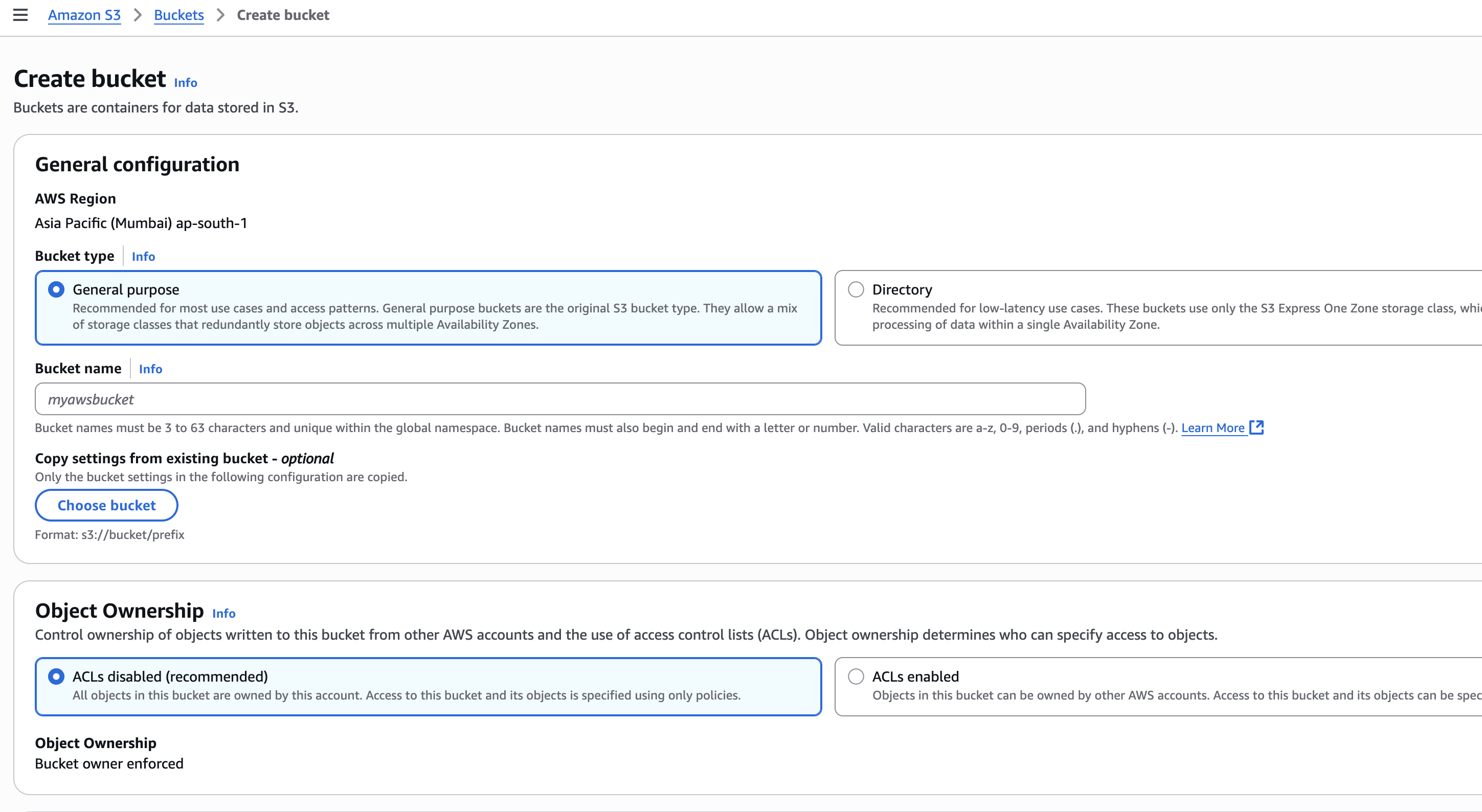

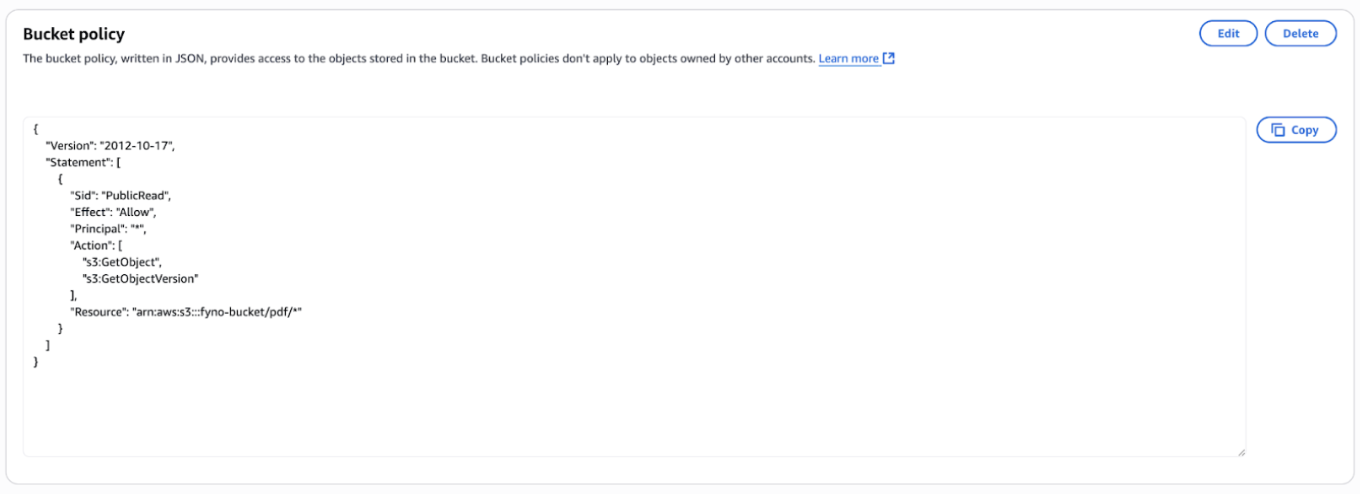
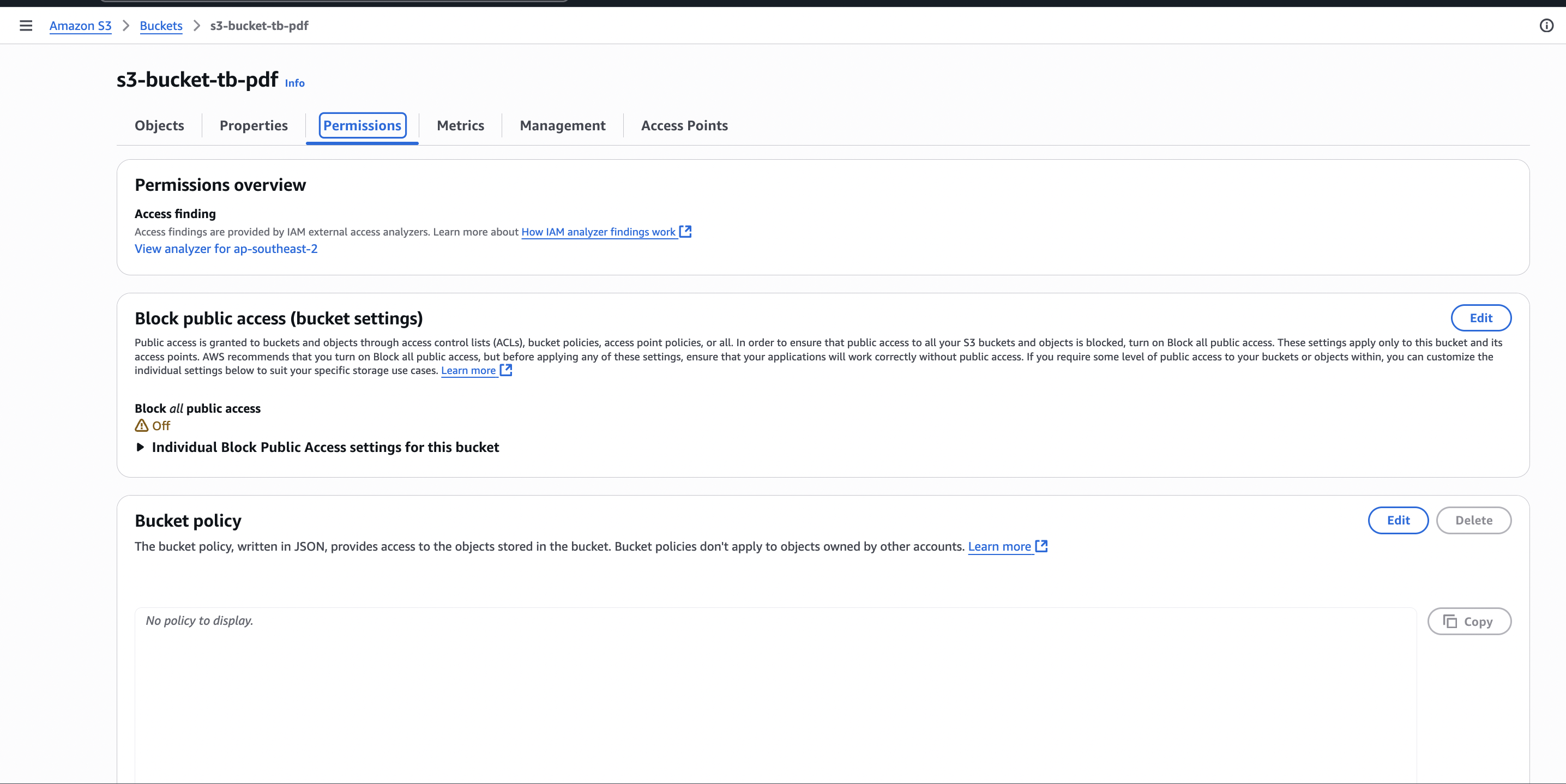
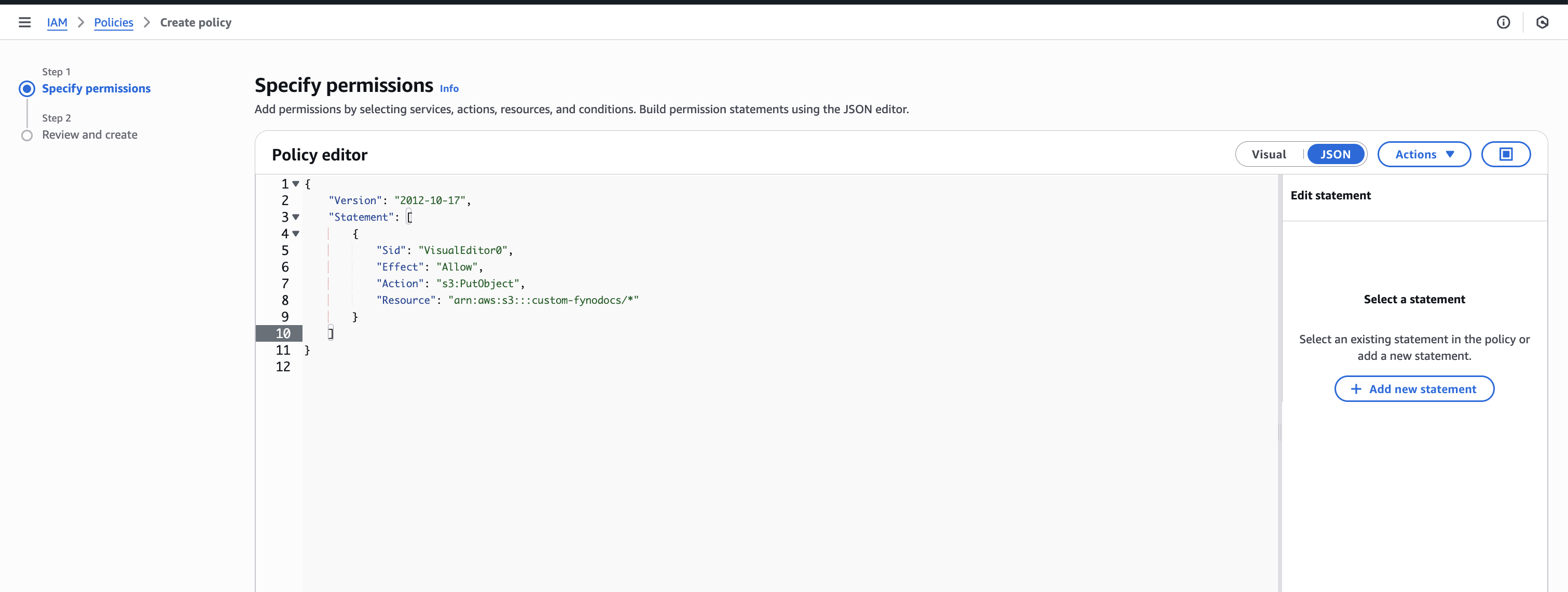
How to make S3 bucket private
To make the S3 bucket private, you need to create a Cloudfront URL and access the S3 bucket using it.
To enable the Secure Media Storage feature for your account,
How to configure for Fyno generated PDFs
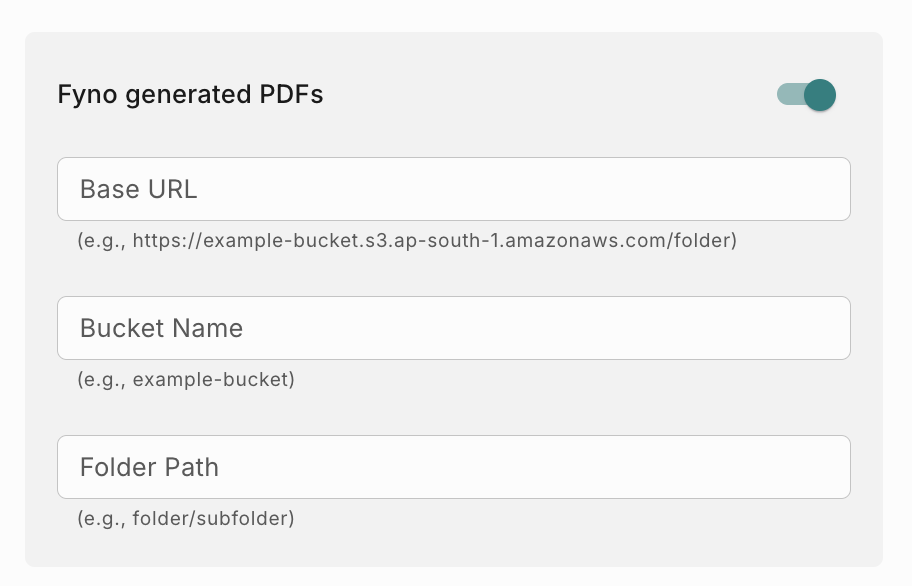
- Base URL : Provide the URL where the Fyno generated PDF files will be stored in this format - <base_url>/<folder>/<subfolder> Example - https://example-bucket.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/pdf/lrn . If you are using CloudFront URL to access S3 bucket and if you have added origin path as /pdf, then you need to add <Distribution_Domain_name>/<subfolder>. Example - abcdefgh.cloudfront.net/lrn
- Bucket Name : Provide the bucket name where the files will be stored.
- Folder Path : Provide the Folder path where the files will be stored. Example - pdf/lrn.
How to configure for Incoming Media

- Base URL : Provide the URL where all the incoming media files (pdf, jpeg, png etc) will be stored in this format - <base_url>/<folder>/<subfolder>. Example - https://example-bucket.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/incoming/media . If you are using CloudFront URL to access S3 bucket and if you have added origin path as /incoming, then you need to add <Distribution_Domain_name>/<subfolder>. Example - abcdefgh.cloudfront.net/media.
- Bucket Name : Provide the bucket name where the files will be stored.
- Folder Path : Provide the Folder path where the files will be stored. Example - incoming/media.
Authentication
Fyno supports multiple authentication mechanisms to securely manage access across organizations.
Supported Authentication Options
Social Login (Google, Microsoft)
Social Login enables authentication using third-party identity providers such as Google and Microsoft.
This method simplifies credential management and accelerates user onboarding by eliminating the need to create and remember separate passwords.
SAML Single Sign-On (SSO)
SAML-based Single Sign-On (SSO) allows authentication through an organization’s existing Identity Provider (IdP), offering centralized access control and enhanced security.
Users can log into Fyno using corporate identity tools such as OKTA, AWS, or other SAML-compliant IdPs.
Once SSO is enabled, all workspace members are redirected through the IdP login flow, ensuring secure and policy-driven access management across the organization.
To learn more, visit the SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) documentation.
Important Note:
SAML SSO is available only on the Enterprise plan.
To enable SSO for your organization, contact Fyno Support at support@fyno.io.
Support assistance includes:
- Enabling SAML SSO for the account.
- Providing a step-by-step setup guide based on your company’s IdP.